HS-LS4-2
Construct an explanation based on evidence that the process of evolution primarily results from four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the heritable genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for limited resources, and (4) the proliferation of those organisms that are better able to survive and reproduce in the environment.
-
 Humans
HumansBy not including everyone, genome science has blind spots
Little diversity in genetic databases makes precision medicine hard for many. One historian proposes a solution, but some scientists doubt it’ll work.
-
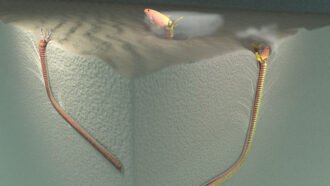 Animals
AnimalsGiant worms may have hidden beneath the ancient seafloor to ambush prey
Twenty-million-year-old tunnels unearthed in Taiwan may have been home to creatures similar to today’s monstrous bobbit worms.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists Say: Evolution
Evolution is how species change over time. Individuals in the group vary, and some will pass on their genes. Over time, the whole species changes.
-
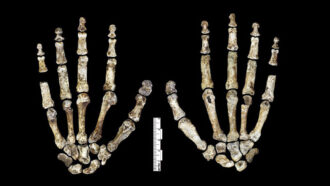 Humans
HumansLet’s learn about early humans
Homo sapiens are the last member left of our genus. But many other species of early humans existed before us.
-
 Fossils
FossilsTube-dwelling sea creatures may be oldest known parasites
A fossil bed of clam-like animals from a half-billion years ago is covered in tube-dwelling organisms. These suggest the tube dwellers were parasites, scientists now report.
-
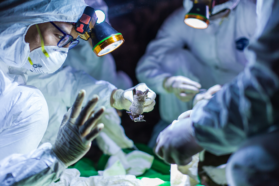 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to find the next pandemic virus before it finds us
Wild animals carry viruses that can sicken people. Monitoring those viral hosts that pose the greatest risk might help prevent a new pandemic.
-
 Fossils
FossilsThis dinosaur was no bigger than a hummingbird
The skull of one of these ancient birds — the tiniest yet known — was discovered encased in a chunk of amber originally found in Myanmar.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnalyze This: Shimmering colors may help beetles hide
Delve into data showing how brilliant colors that shift as a viewer — or predator — moves may help iridescent insects blend in.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmune arms-race in bats may make their viruses deadly to people
An overactive immune system may help bats avoid being sickened by many viruses. This may viruses becoming stronger — and deadlier — when they hit other species.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe many challenges of corralling a coronavirus outbreak
The Chinese government has quarantined millions of people in hopes of limiting spread of a new coronavirus. But no one yet knows how much this will help.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSerious virus emerges in China and is spreading globally
A new viral infection emerged in December 2019 among people in Wuhan, China. The mystery illness has already killed at least 17 people and sickened many hundreds.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGlobetrotting microbes in airplane sewage may spread antibiotic resistance
Along with harder-to-kill microbes, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of the genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.