Matter and Its Interactions

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: What are fats?
A fat molecule's three long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms repel water, stash energy and keep living things warm — even in the bitter cold.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists Say: Decay
This word can refer to rotting flesh or the transformation of radioactive atoms.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about glass
Unlike the atoms in other solids, the atoms in glass don’t exist in an orderly crystal structure. They’re more jumbled up, like the atoms inside liquids.
-
 Tech
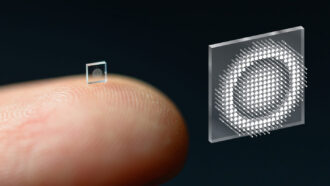
TechThis crumb-sized camera uses artificial intelligence to get big results
Researchers have developed a camera the size of a coarse grain of salt that takes amazingly clear photos.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySnail slime + gold could boost the power of sunscreens and more
These two strange ingredients could make skin-care products that are better for both our skin and the environment.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: What is a metal?
Metals can bend and pull without snapping, and conduct electricity. The reason: Their atoms tend to lose electrons to neighboring atoms.
-
 Materials Science
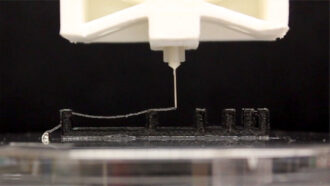
Materials ScienceAnalyze This: This material for 3-D printing is made by microbes
Bacteria with tweaked genes pump out proteins that can be used in a 3-D printer. With microbes in the mix, the living ink can make drugs or suck up chemicals.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Silicon
The chemical element silicon is used to make everything from bricks to cookware to electronics.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCould reusable ‘jelly ice’ cubes replace regular ice?
These hydrogel “jelly ice cubes” are made mostly of gelatin and water. They won’t melt, even when thawed, and may provide new food cooling options.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThis glitter gets its color from plants, not a synthetic plastic
In the new material, tiny arrangements of cellulose reflect light in specific ways to create vibrant hues in an environmentally friendly glitter.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentA new way to make plastics could keep them from littering the seas
Borrowing from genetics, scientists are creating plastics that will degrade. They can even choose how quickly these materials break down.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGenes point to how some bacteria can gobble up electricity
A new study shows how some microbes absorb and release electrons — a trait that may point to new fuels or ways to store energy.