MS-ESS1-4
Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth's 4.6-billion-year-old history.
-
 Space
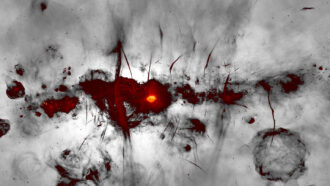
SpaceWild art? No, it’s a radio image of the heart of our Milky Way
Eyelash-like radio filaments accent the brightest feature in this image — a supermassive black hole.
-
 Space
SpaceExplainer: Telescopes see light — and sometimes ancient history
Different kinds of telescopes on Earth and in space help us to see all wavelengths of light. Some can even peer billions of years back in time.
By Trisha Muro -
 Space
SpaceThe long-awaited James Webb Space Telescope has a big to-do list
The James Webb Space Telescope has been in the works for so long that new fields of science have emerged for it to study.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: The age of dinosaurs
Take a trip back to the Mesozoic Era to explore how geologic events, ecosystems and evolution were connected during the so-called age of dinosaurs.
By Beth Geiger -
 Planets
PlanetsNASA’s Perseverance rover grabbed its first Martian rocks
Two finger-sized pieces of stone drilled from a basalt rock are the first bits of Mars ready to be brought to Earth.
-
 Earth
EarthScientists Say: Anthropocene
Humans are changing the world in profound ways. Some scientists think those changes have launched a new epoch in Earth’s history: the Anthropocene.
-
 Animals
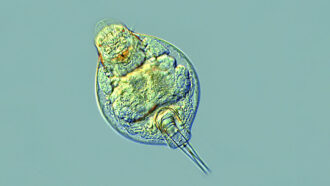
AnimalsTiny animals survive 24,000 years in suspended animation
Tiny bdelloid rotifers awake from a 24,000-year slumber when freed from the Arctic permafrost.
-
 Space
SpaceCosmic filaments may have the biggest spin in outer space
These rotating threads of dark matter and galaxies stretch millions of light-years. Scientists want to know how their spin begins.
-
 Plants
PlantsDinosaur-killing asteroid radically changed Earth’s tropical forests
The asteroid collision initially reduced the diversity in what had been sunny tropical rainforests. In time, the forests would become permanently darker.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExtreme pressure? Diamonds can take it
Diamond retains its structure even at extreme pressures, which could reveal how carbon behaves in the cores of some exoplanets.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Stars and their families
Most pinpoints that light the night sky are raging infernos we call stars. As adults, many will create new elements that they later cast off into the cosmos.
By Ken Croswell -
 Space
SpaceSpotted: Milky Way’s giant gas bubbles in visible light
The bubbles have different colors, based on how the gas inside them moves. That could give clues to how the bubbles developed.