MS-ESS2-6
Develop and use a model to describe how unequal heating and rotation of the Earth cause patterns of atmospheric and oceanic circulation that determine regional climates.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Winds and where they come from
Temperature and pressure are critical factors affecting why the wind blows where it does. Understanding the nature of wind can teach us a lot about weather.
-
 Earth
EarthExplainer: Hurricanes, cyclones and typhoons
Hurricanes are some of the most destructive forces on the planet. Here’s how they form and why they are so dangerous.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists Say: Albedo
To measure how much light reflects off an object, scientists measure its albedo.
-
 Climate
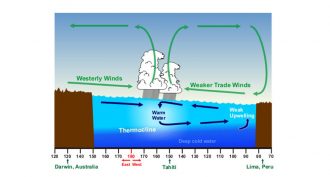
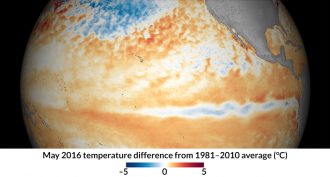
ClimateLast year’s strong El Niño is gone. Next up: La Niña
The 2015 to 2016 El Niño was one of the three strongest on record. It’s now over. Climate experts now predict a La Niña is on its way.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming’s role in extreme weather
Extremes in temperature and precipitation will be more common as global temperatures rise. Human-led climate change is largely to blame, a new study finds.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateFast sea level rise is a very recent change
Sea levels have been rising for more than a century. But that rise is now speeding up. That suggests that what is driving the rise — climate change — also has increased dramatically in recent years.
-
 Climate
ClimateExplainer: Why a tornado forms
Tornadoes start with a thunderstorm. But they also require other ingredients, such as instability.
-