MS-ESS3-3
Apply scientific principles to design a method for monitoring and minimizing a human impact on the environment.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentInsecticide can change a spider’s personality
A chemical meant to kill moths affects the behavior of some spiders. It alters the spiders’ ability to capture prey — including those moths.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureOrganic food starts to prove its worth
Organic food often comes with a higher price. But research is showing that food grown this way can be better for the environment — and possibly for us.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in ivory pinpoints elephant poaching hot spots
Thousands of elephants have been killed for their ivory tusks. A new study used DNA in ivory to trace where most of the killings happen.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Plants
PlantsUsing plants to solve environmental problems
Problems in their communities suggested good research projects to three teens. Each wanted to tackle a different issue, from pollution to world hunger. To learn more about these issues, they turned to their local ponds, wetlands and gardens.
-
 Space
SpaceCollecting trash in space
Space junk threatens satellites that cost millions of dollars. But one teen has come up with an idea to collect and dispose of that orbiting trash.
By Sid Perkins -
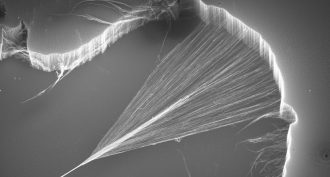 Tech
TechCool Jobs: Big future for super small science
Scientists using nanotechnology grow super-small but very useful tubes with walls no more than a few carbon atoms thick. Find out why as we meet three scientists behind this huge new movement in nanoscience.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureDitching farm pollution — literally
An Indiana project shows how fighting fertilizer runoff can save farmers money, protect wild habitats and prevent harmful algae blooms.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentScientists Say: Microplastic
Bits of plastic smaller than five millimeters are called microplastics. They can end up in the ocean, where corals might mistake them for food.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCorals dine on microplastics
Plastic in the ocean is a growing problem. New research finds that corals may eat tiny bits of plastic, prompting new concerns about the health of living reefs.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists confirm ‘greenhouse’ effect of human’s CO2
Government scientists link directly, for the first time, a boost in warming at Earth’s surface to increasing levels of carbon dioxide. Much of that gas has been released by human activities, such as coal burning and gas-burning vehicles.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHellbenders need help!
Hellbenders already face threats such as habitat loss, pollution and disease. But climate change could make matters worse. And the problems facing hellbenders could spell trouble for more than just these giant amphibians.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentNature documentary puts people in the picture
Many nature documentaries cut people out of the frame. A new series aims to show how we are entwined with our environments.