MS-LS1-2
Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of cells contribute to the function.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: DNA hunters
Snippets of DNA can be left behind by a passing organism. Some researchers now act as wildlife detectives to identify the sources of such cast-off DNA.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: Why scientists sometimes ‘knock out’ genes
How do we learn what a particular molecule does in the body? To find out, scientists often 'knock out' the gene that makes it. Here’s how.
-
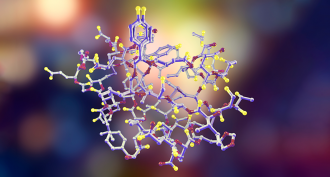 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is a hormone?
Various tissues secrete special chemicals, known as hormones. They travel, usually in blood, to a particular distant site where they tell certain cells it’s time to go to work.
By Janet Raloff -
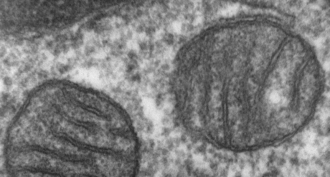 Life
LifeScientists Say: Mitochondrion
Mitochondria are structures inside cells that converts certain chemicals into adenosine triphosphate — a molecule cells use as energy.
-
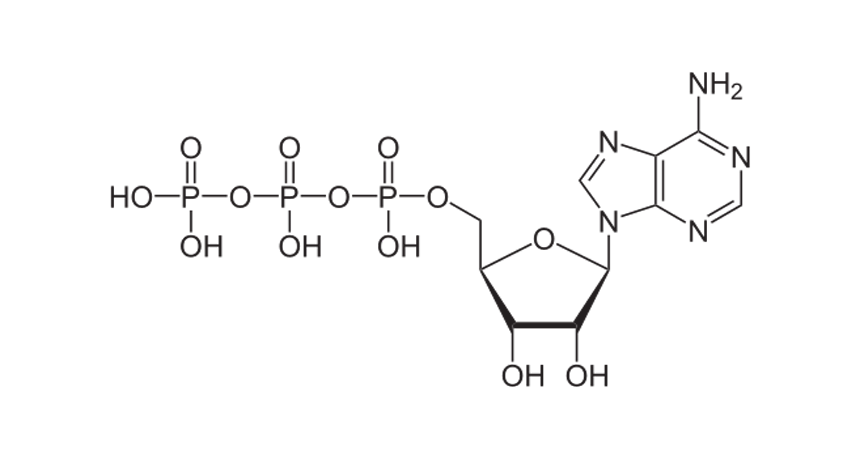 Life
LifeScientists Say: ATP
This chemical is a bit like a rechargeable battery. Cells build and break apart its chemical bonds to store and release energy.
-
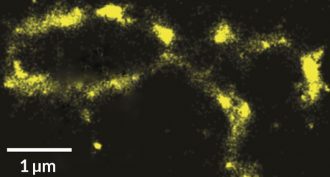 Genetics
GeneticsHow to view tiny parts of DNA? Make them ‘blink’
A new technique can image nanoscale structures in cells without hurting them. No dyes needed. All you have to do is stimulate them with the right color of light.
-
 Life
LifeHow to make a ‘three-parent’ baby
Scientists combined an egg, sperm and some donor DNA: The end result: what appears to be healthy babies.
-
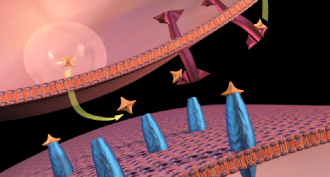 Brain
BrainExplainer: What is dopamine?
Dopamine is a chemical messenger that carries signals between brain cells. It also gets blamed for addiction. And a shortage of it gets blamed for symptoms of diseases such as Parkinson’s.
-
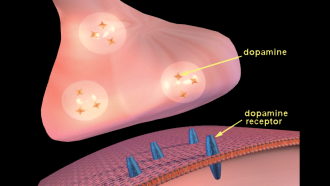 Brain
BrainExplainer: What is neurotransmission?
When brain cells need to pass messages to one another, they use chemicals called neurotransmitters. This sharing of chemical secrets is known as neurotransmission.
-
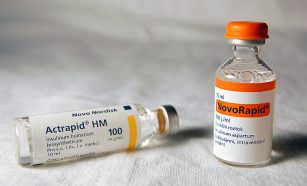 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Insulin
This chemical is a lifesaver. It helps our bodies use the sugars from our food, and without it, people develop diabetes.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentVaping may put your smile at risk
As e-cigarette use among teens rises, scientists find that vaping may cause cellular damage to the mouth, gums and teeth. Even the cells’ DNA was affected.
-
 Life
LifeScientists Say: Autophagy
Cells can break down and recycle their parts for later use. This process — called autophagy — won a scientist a Nobel Prize in 2016.