MS-LS1-8
Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories.
-
 Life
LifeScientists discover itch-busting cells
A study in mice finds the body has a special way of dealing with an itch that’s caused by a light touch. The results could lead to treatments for chronic itch.
-
 Brain
BrainMales and females respond to head hits differently
Men and women are playing sports equally — and getting concussions in comparable numbers. But how their brains respond may differ greatly.
-
 Tech
TechNew light on brain science
A combination of physics, biology and engineering lets scientists use light to trigger actions by specific brain cells. Called optogenetics, this technology is shining new light on how the brain works.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyFriends’ good moods can be contagious
Good mental health spreads through teen social networks, but depression doesn’t, a new study finds.
-
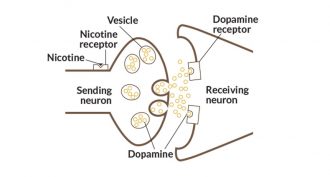 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: The nico-teen brain
Both e-cigarettes and tobacco products can release large amounts of nicotine during use. Nicotine is the chemical that makes tobacco addictive — and the teen brain is especially vulnerable to it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSugar makes mice sleepy
Sugar may amp up sleep-promoting cells in the brain, a new study in mice finds.
-
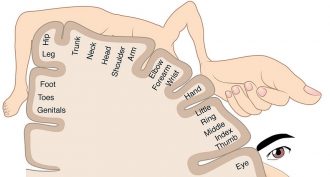 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Cortical homunculus
If you draw a representation of your body as seen by your brain, it’s called a homunculus. On it, parts sensitive to touch or used for fine movement are large, while others are small.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVision-ary high tech
New devices are being developed to improve, restore or preserve the vision of people with eye diseases, such as glaucoma and macular degeneration. One device is a telescopic contact lens than can be zoomed with a wink.
By Sid Perkins -
 Brain
BrainBlowing up the brain
When added to brain tissue, a chemical like one found in baby diapers expands. And it expands that brain tissue too, giving scientists a better view of how its cells connect.
-
 Brain
BrainHarry Potter reveals secrets of the brain
Figuring out how the brain makes sense of what we read isn’t easy. So scientists enlisted the magical world of Harry Potter. It allowed experts to predict with great accuracy which brain areas would be active in a given part of the story.
-
 Brain
BrainScents may affect how appealing tobacco is
Menthol’s effects on the brain may make tobacco more addicting. In contrast, foul odors might help smokers quit. Two new studies show how.
-
 Brain
BrainLearning rewires the brain
Brain cells actually change shape as we learn. It’s one way we cement new knowledge. And much of the action happens as we sleep.