MS-LS1-8
Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories.
-
 Brain
BrainPuberty may reboot the brain and behaviors
Facing adversity early in life can hurt how children learn to deal with stress. Puberty can sometimes offer a chance to reset how the body responds to stress, returning it to normal.
-
 Brain
BrainYou don’t see as much color as you think
It might seem like we live in a world full of color. But when scientists flip it into black and white, most people never notice the switch.
-
 Animals
AnimalsViral scents? Dogs sniff out coronavirus in human sweat
Researchers train dogs to sniff out COVID-19. In the United Arab Emirates, sniffer dogs have already begun identifying infected passengers at airports.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan we taste fat? The brain thinks so
Scientists had not considered fat a 'taste.' The brain begs to differ, new data show.
-
 Brain
BrainExplainer: How our eyes make sense of light
It takes a lot for images before the eyes to be 'seen.' It starts by special cells sensing the light, then signals relaying those data to the brain.
-
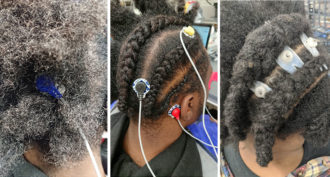 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBrainwaves of people with coarse, curly hair are now less hard to read
Electrodes weren’t designed for people with coarse, curly hair. A redesign was needed, scientists say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsConservation is going to the dogs
Scientists are now training dogs to help track rare, elusive — and sometimes invasive — plants and animals.
-
 Brain
BrainZapping the brain may make it work right again
Sending electrical zaps to electrodes implanted deep in the brain can help people with Parkinson’s disease, depression and even obsessive-compulsive disorder.
-
 Brain
BrainDo you sleep enough to banish unpleasant moods?
A large, long-term study in kids has linked getting too little shuteye with mood and behavior problems.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineConcussions leave clues in the blood
Athletes who suffered concussions had increased blood levels of three proteins. These proteins appear to be a chemical sign of the brain injury.
-
 Brain
BrainEasily distracted? Training your brain’s activity could help
People can train their brainwaves to direct their attention, scientists have now shown. The technique may someday be able to help people focus.
-
 Brain
BrainCuriosity drives this neuroscientist and artist
Christine Liu studies the brain on nicotine — and used Instagram to bring together women doing incredible science.