MS-LS1-8
Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What are allergies?
Sometimes the body’s immune system works too well, like a smoke alarm that blares every time you cook pizza. The results can range from uncomfortable to potentially life-threatening.
-
 Humans
HumansTesting the power of touch
We pet dogs with our fingers, not our arms or backs. Our fingers are more sensitive to touch. But how do we know? Here's how you can test that.
-
 Tech
TechViewing virtual reality of icy landscapes may relieve pain
Traveling to polar vistas via virtual reality eased a temporary burning in the viewers’ skin. The same VR also lessened simulated chronic pain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaping emerges as possible trigger for seizures
Anonymous accounts have been filed with the FDA reporting seizures in teens after vaping. These were linked most often to JUUL and related pods.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe science of ghosts
One in five Americans say they’ve encountered a ghost. But science has no evidence that ghosts are real. Here are more likely explanations.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is the vagus?
The vagus nerve runs from the brain all through the body. It controls many basic functions, including how fast the heart beats.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOwww! World’s hottest chili leads to days of severe headaches
A man ate one of the hottest peppers in the world. About a minute later, his head began pounding. See why they didn’t permanently disappear for days!
By Dan Garisto -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is a concussion?
A concussion is a severe type of head injury that can damage a brain for weeks to years — perhaps even a lifetime.
-
 Brain
BrainTongues ‘taste’ water by sensing sour
Water doesn’t taste like much, but our tongues need to detect it somehow. They may do it by sensing acid, a new study shows.
-
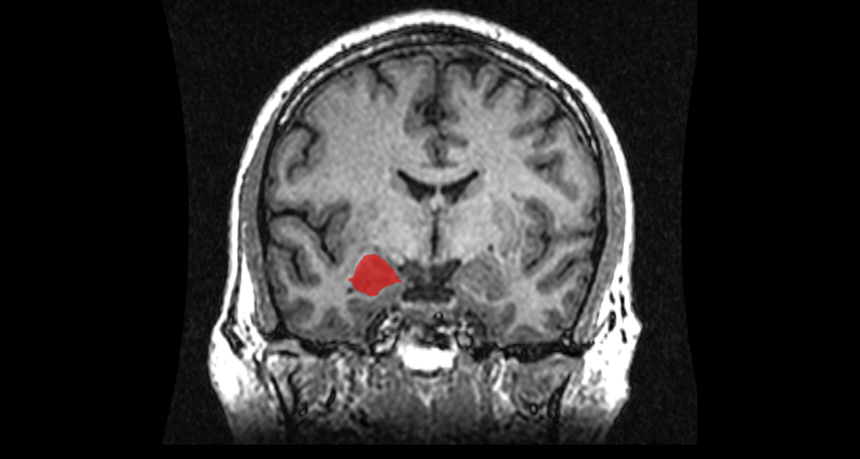 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Amygdala
Named after the Greek word for “almond,” the amygdala helps us process emotions, make decisions and form memories.
-
 Brain
BrainBrains learning together act the same
When students are all focused on the same thing, their brainwaves look the same, a new study shows.
-
 Brain
BrainWhen is an epileptic seizure about to strike?
Two high-school research projects suggest ways to identify early warnings of a coming epileptic seizure. This might give people time to free themselves from potentially dangerous activities.
By Sid Perkins