MS-LS2-1
Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMeet scientists who take on the study of life
What does a scientist look like? Meet these amazing women in biology.
-
 Earth
EarthSeafloor hosts surprising number of deep-sea vents
A new sensor detects changes in seawater chemistry and finds far more ecosystem-supporting seafloor vents than scientists had believed were out there.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFighting big farm pollution with a tiny plant
Fertilizer runoff can fuel the growth of toxic algae nearby lakes. A teen decided to harness a tiny plant to sop up that fertilizer.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertals: Ancient Stone Age builders had tech skills
Neandertals built stalagmite circles in a French cave 176,500 years ago. These structures show that these ancient human cousins had social and technical skills.
By Bruce Bower -
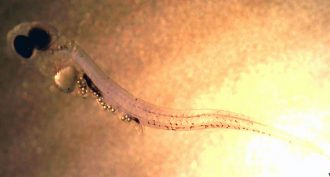 Environment
EnvironmentUh oh! Baby fish prefer plastic to real food
Given a choice, baby fish will eat plastic microbeads instead of real food. That plastic stunts their growth and makes them easier prey for predators.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe shocking electric eel!
Electric eels are fascinating animals. Their powerful zaps can act like a radar system, trick fish into revealing their location and then freeze their prey’s movements.
By Roberta Kwok -
 Environment
EnvironmentWildlife forensics turns to eDNA
Environmental DNA, or eDNA, tells biologists what species have been around — even when they’re out of sight or have temporarily moved on.
-
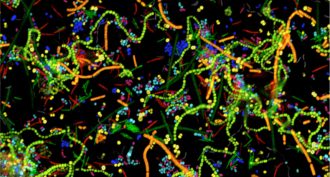 Microbes
MicrobesSlime cities
Biofilms are like tiny cities of bacteria — some harmless, others destructive. Scientists are learning how to keep these microscopic metropolises under control.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPesticides offer bees a risky allure
Honeybees and bumblebees sometimes cannot taste or avoid pesticides called neonicotinoids. And that may expose some of these important pollinators to harm.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesLife’s ultra-slow lane is deep beneath the sea
Biologists had suspected the deep seafloor would be little more than barren sediment. But they found a surprising amount of oxygen — and life.
By Beth Geiger -
 Animals
AnimalsNews Brief: Rabbit-hunting pythons are altering Everglades
Rabbits may breed rapidly, but not fast enough to compensate for the huge summer appetites of huge pythons roaming Florida’s Everglades.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsDesert plants: The ultimate survivors
Creosote, mesquite and other desert plants rely on different adaptations to thrive, even when no rain falls for an entire year.