MS-LS2-2
Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems.
-
 Animals
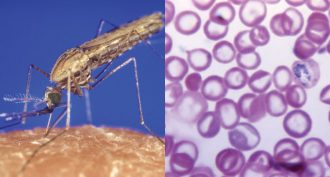
AnimalsMalaria parasites lure mosquitoes to infected hosts
Malaria parasites leave behind an alluring molecule in their hosts’ blood. It draws mosquitoes to sip it, helping spread the disease these carry.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCool Jobs: Abuzz for bees
These scientists are keeping bees healthy, making medicines for people from honey and constructing bee-inspired robots.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyShrimp on treadmills? Some science only sounds silly
Research that may seem silly, at first glance, often has a rewarding aim. Here are some examples.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsUnder blanket of ice, lakes teem with life
Life under frozen lakes is vibrant, complex and surprisingly active, new research finds. In fact, some plants and animals can only live under the ice. But with climate change, will that continue?
-
 Psychology
PsychologyWhat makes a pretty face?
Beautiful faces are symmetrical and average. Do we prefer them because this makes them easier for our brains to process?
-
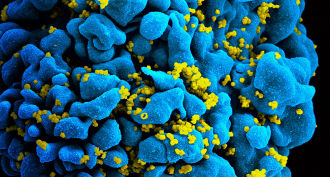 Microbes
MicrobesNew date for U.S. arrival of the AIDS virus
A new study shows that HIV started circulating at least a decade earlier than previously realized.
-
 Oceans
OceansBeaches can be a germy playground
Infectious microbes can flourish on sandy beaches. Scientists are now exploring how to find and monitor these hotspots for pollution that can make vacationers sick.
-
 Oceans
OceansCreative ways to help coral reefs recover
Coral reefs are under siege from threats ranging from climate change to explosives. But scientists are developing ways to rebuild reefs before they disappear.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureBananas under attack: Understanding their foes
Fungal blights threaten the world’s most popular fruit. But genetic studies hint at new ways to combat some of these diseases.
-
 Plants
PlantsScientists Say: Bromeliad
Bromeliads are plants with long spiky leaves. They are common houseplants, and we even see one in the grocery store — the pineapple.
-
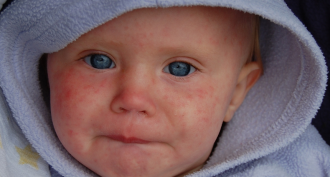 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles in the Americas: Going, going — gone!
The Americas have at last shed a major childhood scourge: measles. The viral infection used to kill hundreds of children each year. Now the hemisphere only sees cases spread by travelers.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZebra finches can ‘drink’ water from their own fat
When water is scarce, thirsty zebra finches can produce their own water. They do it by breaking down their body fat.
By Susan Milius