MS-LS2-2
Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen a species can’t stand the heat
When temperatures rise, New Zealand’s tuatara produce more males. With global warming, that could leave the ancient reptile species with too few females to avoid going extinct.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: How invasive species ratted out the tuatara
The introduction of rats to New Zealand led to huge population losses of the ancient tuatara. These uncommon reptiles vanished from the mainland. This left isolated populations to survive on several dozen isolated islands.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKangaroos have ‘green’ farts
The farts and belches of these animals contain less methane than do those from other big grass grazers. Microbes in their digestive tract appear to explain the ‘roos lower production of this greenhouse gas, a new study finds.
-
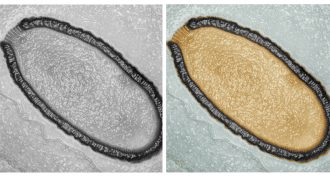 Microbes
MicrobesReturn of the giant zombie virus
Scientists have discovered a new type of virus in Siberian soils. It's the largest virus ever discovered. And guess what: It could infect cells even after 30,000 years in cold storage.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome of chocolate’s health benefits may trace to ‘bugs’
Dark chocolate offers people a number of health benefits. A new study finds that the breakdown of chocolate by microbes in the human gut be behind some benefits.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIntel STS finalist finds new flu fighters
Intel Science Talent Search finalist Eric Chen used a computer simulation to narrow down chemical targets to fight influenza. The drugs that he identified could be the next big weapons against flu.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassing diseases from bee to bee
A study finds that the viruses and parasites that plague honeybees can infect bumblebees too, sickening another important pollinator.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Crazy’ ant fight
By neutralizing the poison produced by fire ants, ‘crazy’ ants can survive heated battles. And that may help explain why crazy ants are edging out fire ants in parts of the southern United States.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFirst living fish leaves ‘endangered’ list
Twenty-one years ago, a minnow facing a high risk of extinction was placed on the U.S. Endangered Species List. With help from scientists, the fish appears to have largely recovered. It’s the first ‘listed’ fish to do so.
-
 Animals
AnimalsExplainer: Animals’ role in human disease
Wildlife, livestock and pets are the source of most germs that can sicken people
-
 Animals
AnimalsInfectious animals
Critters spread many germs that can sicken each other — and even kill people.
-
