MS-LS2-3
Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen a species can’t stand the heat
When temperatures rise, New Zealand’s tuatara produce more males. With global warming, that could leave the ancient reptile species with too few females to avoid going extinct.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentBurning to learn
Fires cause billions of dollars of destruction to homes and forests every year. But not all fires are bad, especially for forests. With a better understanding of fire, scientists can both help people prevent dangerous fires — and identify which ones it would be better to let burn.
-
 Environment
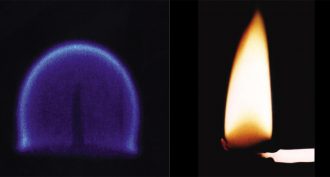
EnvironmentExplainer: How and why fires burn
A fire’s colorful flame results from a chemical reaction known as combustion.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassing diseases from bee to bee
A study finds that the viruses and parasites that plague honeybees can infect bumblebees too, sickening another important pollinator.
-
 Earth
EarthIntel STS finalist brings earthworms to the big time
Earthworms and charcoal help plants resist infections, according to research by Anne Merrill, a finalist in the 2014 Intel Science Talent Search.
-
 Earth
EarthMining metals amidst seafloor animals
Miners may need to get their feet — and everything else — wet as they carefully seek out loads of copper and other valuable natural resources.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthExplainer: Antarctica, land of lakes
There are many, although they tend to be buried under rivers of ice.
By Douglas Fox -
 Chemistry
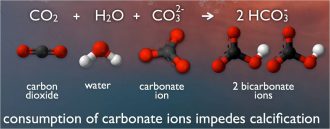
ChemistryExplainer: Ocean acidification
Here’s why shellfish and other animals in the sea suffer when the ocean is forced to absorb too much carbon dioxide.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny earthworms’ big impact
Invasive earthworms change North American landscapes, for better or worse.
-

-
 Oceans
OceansLife beneath the ‘berg
Scientists find Antarctic icebergs play a new and bigger role in the climate cycle.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesLife in the bacterial underground
Tiny life forms in rock may coax minerals to release hydrogen for food.