MS-LS2-3
Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyScience isn’t just for scientists
It doesn’t take an advanced degree or a lab to do science. All you need is curiosity and an interest in learning something new every day.
-
 Earth
EarthStudy appears to rule out volcanic burps as causing dino die-offs
New data on when massive volcanic eruptions happened do not match when the dinosaur mass extinction took place.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsNewfound desert soil community lives on sips of fog
Lichens and other fungi and algae team up to form a 'grit-crust' on the parched soil of Chile’s Atacama Desert. Those species slake their thirst with moisture from coastal fog.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Life
LifeWhy some whales become giants and others are only big
Being big helps whales access more food. But just how big a whale can get is influenced by whether it hunts or filter-feeds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhales echolocate with big clicks and tiny amounts of air
Toothed whales may echolocate using bits of air that they recycle inside their heads to conserve both air and energy.
-
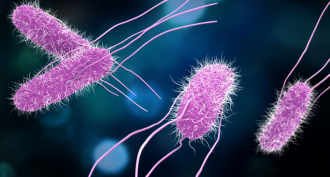 Life
LifeExplainer: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes tend to be small and simple, while eukaryotes have embraced a highly organized lifestyle. These divergent approaches to life have both proved very successful.
-
 Oceans
OceansSmall swimmers may play huge role in churning the seas
Hoards of migrating shrimp and krill can cause large-scale water movements in the ocean, a new study suggests.
-
 Plants
PlantsExplainer: The fertilizing power of N and P
Two elements — nitrogen and phosphorus — help plants grow. When the soil doesn’t have them, farmers might add them in the form of fertilizer.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBee hotels are open for business
Bee hotels are creating a buzz in conservation and research by offering nesting places for wild bees.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTrees can make summer ozone levels much worse
The greenery can release chemicals into the air that react with combustion pollutants to make ozone. And trees release more of those chemicals where it gets really hot, a new study finds.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesWorld’s deepest zoo harbors clues to extraterrestrial life
Scientists have found a wide range of life deep below Earth’s surface. The discoveries could help inform our search for life on other planets.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCool Jobs: New tools to solve crimes
Future investigators may identify criminals by the microbes they leave behind or by using DNA-like evidence from strands of their hair.