MS-LS2-4
Construct an argument supported by empirical evidence that changes to physical or biological components of an ecosystem affect populations.
-
 Tech
TechOur gut microbes love a good workout
Technology shows how microbes in the body respond to exercise. That helps scientists understand why those microbes keep athletes healthy.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPesticides can have long-term impact on bumblebee learning
Pesticide-laced nectar and pollen can permanently harm the brains of baby bumblebees.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMinecraft’s big bees don’t exist, but giant insects once did
Big bees buzz in Minecraft. In our world, blocky bees might starve and be stuck on the ground. Yet long ago, giant insects did roam our planet.
-
 Earth
EarthStudy appears to rule out volcanic burps as causing dino die-offs
New data on when massive volcanic eruptions happened do not match when the dinosaur mass extinction took place.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDrones might one day capture a dolphin’s breath in midair
High-speed footage of dolphin spray reveals that droplets blast upward at speeds close to 100 kilometers per hour.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe many challenges of corralling a coronavirus outbreak
The Chinese government has quarantined millions of people in hopes of limiting spread of a new coronavirus. But no one yet knows how much this will help.
-
 Oceans
OceansHealthy coral reef sounds attract fish searching for a home
Playing the sounds of a healthy reef can help attract fish to dying corals, helping rebuild their community.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAustralian fires have imperiled up to 100 species
As massive wildfires consume huge swaths of Australia’s bush, untold species — many of them found nowhere else — are now threatened with extinction.
-
 Life
LifeWhy some whales become giants and others are only big
Being big helps whales access more food. But just how big a whale can get is influenced by whether it hunts or filter-feeds.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGlobetrotting microbes in airplane sewage may spread antibiotic resistance
Along with harder-to-kill microbes, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of the genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.
-
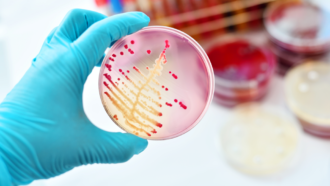 Microbes
MicrobesDrug-resistant germs kill some 35,000 Americans each year
The new mortality rate may be way low, some experts say. Also troubling are two new germs that have emerged as big and urgent threats.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHunting hidden salamanders with eDNA
The Japanese clouded salamander is an elusive beast. To find a new population, three teens turned to high-tech methods.