MS-LS3-1
Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes (mutations) located on chromosomes may affect proteins and may result in harmful, beneficial, or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism.
-
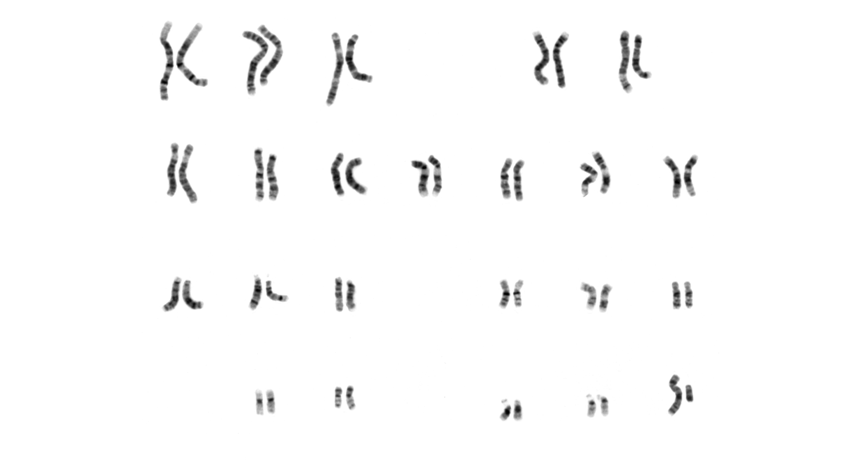 Genetics
GeneticsScientists Say: Chromosome
This threadlike structure is made of DNA wrapped around protein. It allows the 3 billion base pairs in human DNA to stay neatly packaged in a cell.
-
 Tech
TechTweaked germs glow to pinpoint buried landmines
Finding landmines could become much safer with a new technology. It uses genetically modified bacteria that glow under laser light.
By Dinsa Sachan -
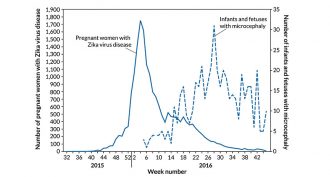 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnalyze This: Zika and microcephaly
Data from pregnant women with Zika in Colombia helped scientists probe whether Zika causes birth defects.
-
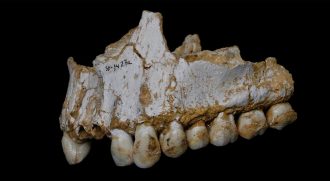 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFossils point to Neandertal diets — and medicine use
Whether Neandertals were largely meat-eaters or vegans depended on their environment, fossils now suggest. Their teeth also indicate they used natural medicines.
-
 Life
LifeHow to make a ‘three-parent’ baby
Scientists combined an egg, sperm and some donor DNA: The end result: what appears to be healthy babies.
-
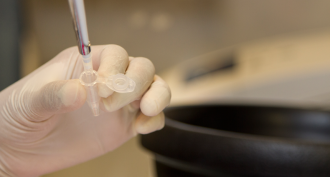 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: How PCR works
The polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, is like a DNA-copying machine. It duplicates genetic material over and over. Here’s how.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists find genes that make some kids’ hair uncombable
Scientists have pinpointed three genes that cause ‘uncombable hair syndrome’ in some kids.
By Dinsa Sachan -
 Genetics
GeneticsWorld’s tallest corn towers nearly 14 meters
Short nights and a genetic tweak helped novel corn reach record heights.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika birth defects: Concerns spread from head to toe
Zika infections may trigger problems well beyond babies born with small heads and brains. Scientists have begun linking a range of head-to-toe health ails to the virus.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsTasmanian devils begin to resist infectious cancer
A deadly contagious cancer is spreading among Tasmanian devils. But the animals are evolving resistance, a new study finds.
-
 Life
LifeScientists watch germs evolve into superbugs
To study how bacteria can evolve resistance to a wide variety of drugs, scientists spread the germs on a food-filled plate the size of a foosball table. Then, they watched resistance rise.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureBananas under attack: Understanding their foes
Fungal blights threaten the world’s most popular fruit. But genetic studies hint at new ways to combat some of these diseases.