MS-LS4-2
Apply scientific ideas to construct an explanation for the anatomical similarities and differences among modern organisms and between modern and fossil organisms to infer evolutionary relationships.
-
 Fossils
FossilsMega-bird!
What may have been the bird world’s biggest flier ever had wings so long, they would have had trouble flapping fast enough to keep it aloft in tough winds. But this behemoth would have been able to soar both far and fast.
-
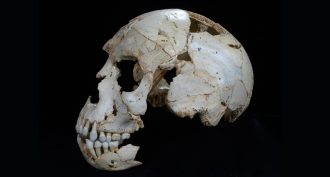 Archaeology
ArchaeologyNeandertal ancestor?
Fossils found in a Spanish cave have features that are a combination of Neandertals and other species. The mix suggests Neandertal roots go back even farther than scientists had suspected.
-
 Fossils
FossilsScary ‘chicken’ roamed Earth with T. rex
Scientists have just pieced together evidence of a weird new dinosaur that sported sharp claws, feathers and a beak. And it just may have been one of the last dinos to roam Earth about 67 million years ago.
-
 Fossils
FossilsReviving dinosaurs
With the help of computers, researchers are getting a pretty good idea of how these ancient creatures moved, walked and ate.
By Sid Perkins -
 Fossils
FossilsWhere do humans come from?
Some scientists propose a newfound South African species as the most likely ancestor of the line that led to humans. But not everyone accepts that this is where it all began.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsThe secret songs of giant beavers
Scientists discover a noisemaking chamber in the extinct animal’s skull.
-
 Humans
HumansMummies share their secrets
Cutting-edge technology such as CT, or CAT, scans and endoscopes are allowing scientists to see not just what’s underneath the wrappings but also what’s inside a mummy’s body.
-
 Humans
HumansOld bones ignite fresh debate
Scientists try to understand how 2 million-year-old fossils fit among ancient species.
-
 Fossils
FossilsDangerous dinos in the dark
Eye fossils reveal predatory dinosaurs’ preference for hunting at night.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentBusy bacteria leave big mark
Earth’s earliest life-forms built mounds on an Antarctic lake bottom.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEating can be skin deep
In the laboratory, bottom-dwelling hagfish absorb nutrients through the skin.
-
