MS-LS4-5
Gather and synthesize information about the technologies that have changed the way humans influence the inheritance of desired traits in organisms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBringing COVID-19 vaccines to much of world is hard
The price of not vaccinating nearly everyone across the world could be a longer pandemic and more troubling variants of the new coronavirus.
-
 Humans
HumansBy not including everyone, genome science has blind spots
Little diversity in genetic databases makes precision medicine hard for many. One historian proposes a solution, but some scientists doubt it’ll work.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHarsh Ice Age winters may have helped turn wolves into dogs
In the Ice Age, Arctic hunters may have turned to some game for their fatty bones. Much of those animals’ meat might have been left to domesticate dogs.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsHere’s how giant pumpkins get so big
Cinderella took a ride in a pumpkin coach. Though real pumpkins do get big enough, here’s why their ride would be uncomfortable at best.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing can alter body fat and may fight diabetes
Researchers have long dreamed of using brown fat to fight obesity and diabetes. Work in animals shows they’re closing in on achieving that dream.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA glowing new way to measure antibodies
Researchers invent a way to detect and measure antibodies with glowing proteins. Antibodies can mark exposure to various diseases.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsA single chemical may draw lonely locusts into a hungry swarm
Swarms of locusts can destroy crops. Scientists have discovered a chemical that might make locusts come together in huge hungry swarms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA Hong Kong man got the new coronavirus twice
His is the first confirmed case of reinfection with this virus. His second bout was detected by accident, because he showed no symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies from former COVID-19 patients could become a medicine
The experimental treatment uses antibodies from the blood plasma of COVID-19 survivors. It may prevent disease in other people or help treat the sick.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSearch speeds up for vaccine against the new coronavirus
Scientists are investigating unusual ways to make drugs to prevent viral infections. One may even be able to treat already sick people.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe many efforts to lick cat allergies
Up to one in five people around the world may be allergic to cats. Science is coming to help their desire for kitty cuddles.
-
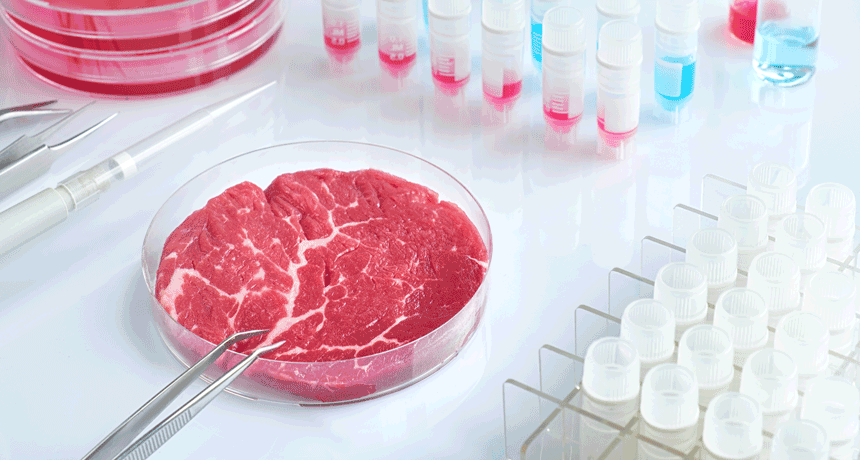 Life
LifeA new spin on lab-grown meat
A technique inspired by how cotton candy is spun could help produce lab-grown meat at a lower cost and on a bigger scale.