MS-LS4-6
Use mathematical representations to support explanations of how natural selection may lead to increases and decreases of specific traits in populations over time.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesGlobetrotting microbes in airplane sewage may spread antibiotic resistance
Along with harder-to-kill microbes, airplane sewage contains a diverse set of the genes that let bacteria evade antibiotics.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesDrug-resistant germs kill some 35,000 Americans each year
The new mortality rate may be way low, some experts say. Also troubling are two new germs that have emerged as big and urgent threats.
-
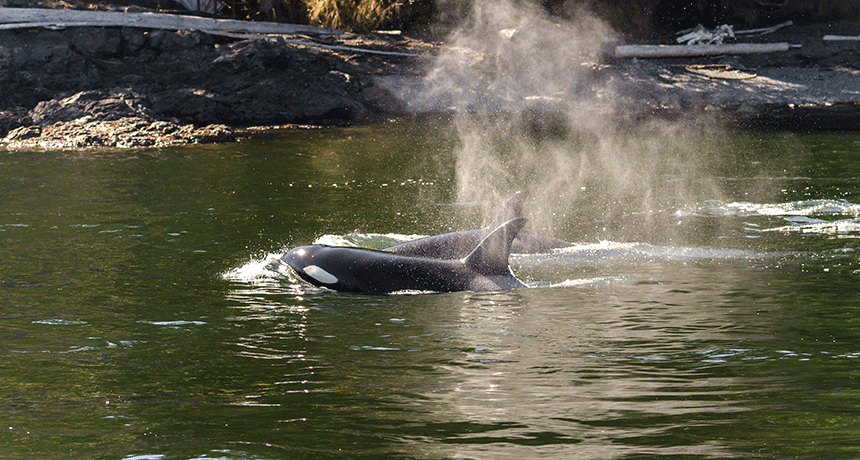 Animals
AnimalsOrca snot leads to a whale of a science-fair project
DNA found in the mucus of orcas suggests that even though the traits of family pods may differ, these marine mammals all appear to belong to a single species.
By Sid Perkins -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is a hormone?
Various tissues secrete special chemicals, known as hormones. They travel, usually in blood, to a particular distant site where they tell certain cells it’s time to go to work.
By Janet Raloff -
 Life
LifeWeird mega-worm found to have odd diet
Giant shipworms have bacteria in their gills that produce food for them. This has made their digestive organs shrink from lack of use.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimals can do ‘almost math’
Humans aren’t the only animals with a number sense. Scientists are trying to figure out where and when it evolved.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsTasmanian devils begin to resist infectious cancer
A deadly contagious cancer is spreading among Tasmanian devils. But the animals are evolving resistance, a new study finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: What is epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of molecular “switches” that turn genes on and off. Tweak those switches and there could be big health consequences.
By Janet Raloff -
 Brain
BrainOur eyes can see single specks of light
The human eye can detect a single photon. This discovery answers questions about how sensitive our eyes are. It hints at the possibility of using our eyes to study issues of quantum-scale physics.
-
 Life
LifeHow a moth went to the dark side
Peppered moths and some butterflies are icons of evolution. Now scientists have found a gene responsible for making them so.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe turning of wolves into dogs may have occurred twice
The process of turning wolves into dogs, called domestication, may have occurred twice — in the East and the West — ancient DNA suggest.
-
 Humans
HumansSlicing meat may have aided human evolution
An experiment with modern-day humans shows how slicing meat could have saved human ancestors energy — and let their bodies and brains get bigger.
By Bruce Bower