MS-LS4-6
Use mathematical representations to support explanations of how natural selection may lead to increases and decreases of specific traits in populations over time.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChikungunya wings its way north — on mosquitoes
A mosquito-borne virus once found only in the tropics has adapted to survive in mosquitoes in cooler places, such as Europe and North America.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Microbes
MicrobesThe bugs within us
Hordes of bacteria live inside people and other animals. This ‘microbiome’ can affect the development of the blood-brain barrier, food choices — even mating.
By Roberta Kwok -
 Animals
AnimalsReturn of the bed bug
Bed bugs have staged a comeback over the past 15 years. The bloodsucking parasites succeeded through a combination of evolution and luck.
By Brooke Borel -
 Animals
AnimalsMates or survival: Which explains a bird’s color?
When male birds are brightly colored, we assume that’s because their plumage attracts the gals. But a new study with thousands of museum specimens shows that sometimes survival is just as important a factor behind bird color.
-
 Physics
PhysicsEyelashes: The ‘sweet’ length
New mathematical and aerodynamics studies find what seems to be the optimal length for eyelashes — the length that protects best. And surprise: Longer is not always better.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsOcean animals have mushroomed in size
Compared to a half-billion year ago, sea creatures are, on average, roughly 150 times bigger, a new study finds.
-
 Fossils
FossilsTar pit clues provide ice age news
New analyses of insects and mammals trapped in the La Brea Tar Pits point to climate surprises during the last ice age.
By Sid Perkins -
 Archaeology
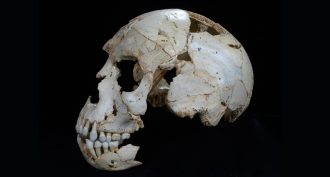
ArchaeologyNeandertal ancestor?
Fossils found in a Spanish cave have features that are a combination of Neandertals and other species. The mix suggests Neandertal roots go back even farther than scientists had suspected.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhen a species can’t stand the heat
When temperatures rise, New Zealand’s tuatara produce more males. With global warming, that could leave the ancient reptile species with too few females to avoid going extinct.
-
 Life
LifeCaught in the act
Scientists observe some evolutionary speed demons as they adapt over the course of just a few years to new environmental conditions.
-

-
 Fossils
FossilsDino teeth tell a traveling tale
Dental evidence from sauropods suggests the mighty beasts migrated for food.