MS-PS1-4
Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: All about the calorie
Calories are a measure of how much energy is in a food. But when it comes to powering our bodies, not all calories are equally available to the body.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: What is a catalyst?
Catalysts are used in manufacturing and many technologies. They’re also found in living things. They help chemical reactions move along.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHere’s how hot water might freeze faster than cold
There’s a new explanation for how hot water freezes faster than cold water. But not everyone agrees it’s right, or that the effect can happen at all.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWeird physics warps nearby star’s light
Scientists have observed a bizarre effect of quantum physics in light coming from a nearby neutron star.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Sublimation
Matter doesn’t always go from solid to liquid to gas. Sometimes it skips a step.
-

Teen studies better cleaning through chemistry
Why do we use hot water and soap to get things clean? To find out, a teen invented a way to measure surface tension.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Absolute zero
Even when we think it’s cold out, most molecules are moving. Only at absolute zero will all of their motions stop.
-
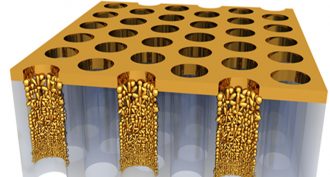 Physics
PhysicsSunlight + gold = steaming water (no boiling needed)
Nano-gold is the new black, at least when it comes to absorbing heat. When tiny gold particles get together, they become energy super-absorbers — turning them black.
-
 Earth
EarthCarbon dioxide could explain how geysers spout
A new study overturns 150 years of thinking about Yellowstone’s geysers. Carbon dioxide, not just hot water, may be driving those spectacular eruptions.
-
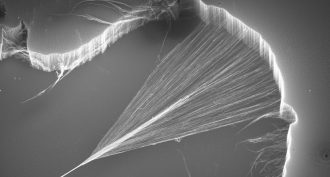 Tech
TechCool Jobs: Big future for super small science
Scientists using nanotechnology grow super-small but very useful tubes with walls no more than a few carbon atoms thick. Find out why as we meet three scientists behind this huge new movement in nanoscience.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNews Brief: As timely as it gets
A newly modified atomic clock won’t lose or gain a second for 15 billion years. This timepiece is about three times more precise than an earlier version.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsHow popcorn got its pop
Popcorn is a popular treat. Now, scientists have learned exactly what happens as it pops. They also have come up with an experiment they hope you will try.