MS-PS1-4
Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed.
-
 Materials Science
Materials Science‘Smart’ windows could save energy
Tiny chemical droplets in a liquid sandwiched between panes of glass turn cloudy when they warm up. This will block some sunlight and potentially save on air conditioning bills.
By Sid Perkins -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceScientists Say: Colloid
When water hovers in the air as fog and when bits of fat disperse in water as milk, they form a type of substance called a colloid.
-
 Tech
TechRewritable paper: Prints with light, not ink
Rewritable paper could save money, preserve forests and cut down on waste — and all without using any ink.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSmooshed diamonds: A window into exoplanets?
Scientists have compressed diamonds more than ever before. Their carbon may give clues to what conditions might be like deep within planets way beyond our solar system.
-
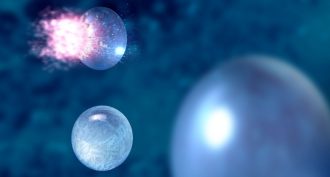 Physics
PhysicsVery-sub-zero water
Using lasers, scientists measured the temperature of water droplets that remained liquid even when super-cold.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWorld’s coolest ‘clock’ is also crazy-accurate
This is the time to beat — the world’s most accurate atomic clock ever. At its heart is a ‘fountain’ of cesium atoms chilled nearly to absolute zero!
By Janet Raloff -
 Physics
PhysicsTemperature ‘lock’ for new hard drives?
A novel material can alter how easy it is to change data stored on it, based on temperature. One immediate application: more secure hard drives for computing.
By Andrew Grant -
 Physics
PhysicsClosing in on fusion energy
Scientists blasted a tiny capsule of hydrogen with laser beams, setting off a reaction that released more energy than in earlier experiments. Still, scientists remain a long way from creating a reaction that releases more energy than it needs to get started.
-

-

-
 Planets
PlanetsPossible new saltwater stains on Mars
Dark streaks that grow in spring, fade in winter may point to saltwater on the Red Planet.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: How a synchrotron works
Giant magnets direct superfast light into beams up to 30 million times as bright as those produced by a laser pointer.
By Emily Sohn