MS-PS4-2
Develop and use a model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through various materials.
-
 Earth
EarthThe Alps’ Matterhorn shows how much even big mountains sway
Such mountain sway data can help planners map high-risk zones for peaks, bridges or any large structures.
By Peg Lopata -
 Earth
EarthVolcanic avalanches may be more destructive than previously thought
Pressures within these pyroclastic flows may be as much as three times as high as observations had suggested.
By Nikk Ogasa -
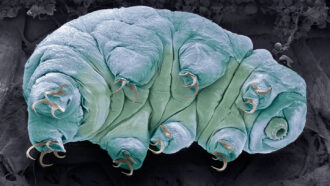 Animals
AnimalsLiving mysteries: Why teeny-weeny tardigrades are tough as nails
Tardigrades often live in cool, damp moss. Their cushy life has somehow prepared them to survive the lethal radiation of outer space.
By Douglas Fox -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLet’s learn about glass
Unlike the atoms in other solids, the atoms in glass don’t exist in an orderly crystal structure. They’re more jumbled up, like the atoms inside liquids.
-
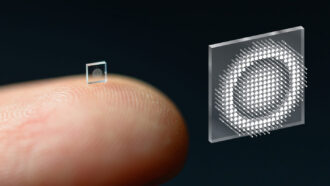 Tech
TechThis crumb-sized camera uses artificial intelligence to get big results
Researchers have developed a camera the size of a coarse grain of salt that takes amazingly clear photos.
-
 Space
SpaceExplainer: Telescopes see light — and sometimes ancient history
Different kinds of telescopes on Earth and in space help us to see all wavelengths of light. Some can even peer billions of years back in time.
By Trisha Muro -
 Space
SpaceThe long-awaited James Webb Space Telescope has a big to-do list
The James Webb Space Telescope has been in the works for so long that new fields of science have emerged for it to study.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySnail slime + gold could boost the power of sunscreens and more
These two strange ingredients could make skin-care products that are better for both our skin and the environment.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThis glitter gets its color from plants, not a synthetic plastic
In the new material, tiny arrangements of cellulose reflect light in specific ways to create vibrant hues in an environmentally friendly glitter.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s why ducklings swim in a row behind mom
Baby ducks save energy by surfing their mother’s waves, but only if they do it in an orderly line.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFuture cars may offer personal sound zones — no earphones needed
Zones that offer each passenger personal listening are closer to reality. A new design improves performance by adapting to the conditions in your car.
-
 Space
SpaceLet’s learn about auroras
A gust of charged particles from the sun called the solar wind lights up auroras on Earth — and on other planets.