Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysics explains why poured water burbles the way it does
The loudness of falling water depends on the height of the pour and the thickness of the stream.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Polarized light
Sunlight, lamplight and other lights are usually unpolarized. But passing light waves through filters can ‘polarize’ them.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNeutrons are unveiling hidden secrets of fossils and artifacts
Images made with these particles have revealed details of dinosaur bones, mummies and more.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAnalyze This: Stonehenge’s ‘Altar Stone’ has mysterious origins
After a century of searching for the source of the Altar Stone, scientists have yet to figure out where ancient people got the rock.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHeat makes water evaporate. Now it appears light can, too
In the lab, shining light on water made it evaporate faster. This never-before-seen effect, if real, might be happening naturally all around us.
-
 Oceans
OceansShading corals during midday heat can limit bleaching
Shading coral reefs during the sunniest part of the day may help corals survive marine heat waves.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA new tool shows tiny changes in the ’24-hour’ length of a day
An underground instrument known as ‘G’ uses laser beams to measure Earth’s rotation — a gauge of day length — with extreme precision.
-
 Tech
TechHow green is your online life?
From the manufacturing of our favorite devices to using them for social interactions, our digital lives can have a big climate impact.
By Sarah Wells -
 Tech
TechBionic plants and electric algae may usher in a greener future
Some can aid the climate by removing pollutants. Others would just avoid dirtying the environment in the first place.
-
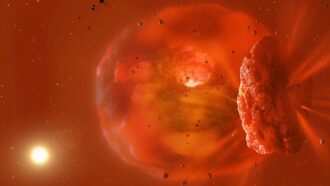 Planets
PlanetsIn a first, astronomers spot the aftermath of an exoplanet smashup
Infrared light from a distant star appears to be leftovers of an impact between a pair of Neptune-sized worlds.
By Elise Cutts -
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Gamma ray
Lightning bolts, nuclear explosions, colliding stars and black holes all throw off this high-energy type of light.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Ultrasonic
This word describes sound waves that have frequencies too high for human ears to hear.