Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Fossils
FossilsIdentifying ancient trees from their amber
A Swedish teen’s analyses of a sample of amber may have uncovered a previously unknown type of ancient tree.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthCool Jobs: Getting to know volcanoes
It’s too hot to explore the insides of a volcano. These scientists examine their lava, their low-frequency rumblings and their ‘vog’.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Computing
ComputingDNA can now store images, video and other types of data
Tiny test tubes might one day replace sprawling data-storage centers, thanks to a new way to encode and retrieve information on strands of synthetic DNA.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeaded to a concert this summer? Pack earplugs
Wearing earplugs at concerts and other loud events may prevent hearing loss and permanent ear damage, a new study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: When loud becomes dangerous
Many people don’t realize that sounds — even those of the music they love — can prove harmful when they get too loud.
By Janet Raloff -
 Tech
TechHow to make window ‘glass’ from wood
Scientists have come up with a way to make wood transparent. The new material could be used in everything from windows to packaging.
By Sid Perkins -
 Physics
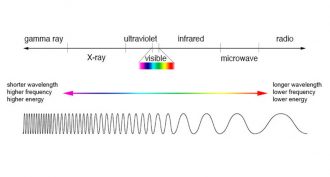
PhysicsScientists Say: Frequency
The distance between one wave peak and another is wavelength. But how fast those peaks are moving along is frequency.
-
 Space
SpaceHurricane at this galaxy’s center is wicked fast
The gale-force winds around one quasar whip by at almost 200 million kilometers per hour. That’s 625,000 times faster than the strongest hurricanes on Earth.
-
 Physics
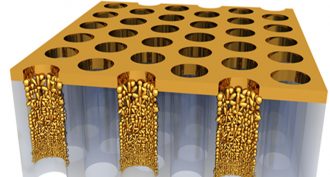
PhysicsSunlight + gold = steaming water (no boiling needed)
Nano-gold is the new black, at least when it comes to absorbing heat. When tiny gold particles get together, they become energy super-absorbers — turning them black.
-
 Earth
EarthCool Jobs: Mapping the unknown
Scientists find different ways of exploring places humans will never visit — and drawing maps to help us better understand such mysterious places.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Tech
TechFeeling objects that aren’t there
A new technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create virtual objects you can feel. Its uses include better video games and safer driving.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists Say: Wavelength
When something travels as a wave — such as light — scientists can measure it by its wavelength, the distances between the peaks.