Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHazing: How to hide in nearly plain sight
A new system takes advantage of a translucent fog of particles to hide otherwise obvious objects.
-
 Tech
TechDigital displays get flexible
Flexible and unbreakable digital displays could soon be for sale, thanks to a new organic transistor made from plastic.
-
 Tech
TechDigital lighting goes organic
An environmentally friendly lighting technology promises not only to save energy but also to transform our indoor environment.
-
 Tech
TechFighting theater pirates
How can theaters thwart thieves from unlawfully recording a movie during a showing? A high-school freshman’s low-cost solution relies on simple physics.
By Sid Perkins -
 Physics
PhysicsStudent radiation experiment goes to space
The Exploration Design Challenge asked students to design shields that would protect astronauts from radiation. Teachers can still involve classes in the challenge.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWorld’s coolest ‘clock’ is also crazy-accurate
This is the time to beat — the world’s most accurate atomic clock ever. At its heart is a ‘fountain’ of cesium atoms chilled nearly to absolute zero!
By Janet Raloff -
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: How lasers make ‘optical molasses’
Light can bump an atom. Bump it from several different directions at once and even a fast-moving atom will instantly freeze its motion — and chill it to a temperature of nearly absolute zero.
By Janet Raloff -
 Physics
PhysicsSending student science to space
Two teachers describe how they worked with the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program to get middle-school scientists excited about research and space.
-
 Physics
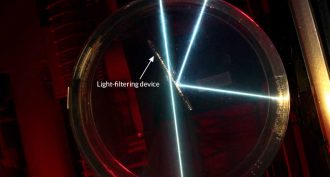
PhysicsFilter lets in only the right light
Scientists have built a light filter that only permits light coming from one desired angle to pass through. Built from alternating layers of transparent materials, it could help minimize the glare in telescopes and cameras or boost the efficiency of solar cells.
-
 Earth
EarthThe quake that shook up geology
North America’s biggest earthquake struck 50 years ago. Here’s what science has learned about Earth since the 1964 Great Alaskan Earthquake.
By Beth Geiger -
 Earth
EarthExplainer: Telling a tsunami from a seiche
Waves that hit coastlines with ferocious power, tsunamis are one of the planet’s most devastating forces of nature. And seiches: They’re tsunamis little, but still potentially deadly, cousins.
-
 Animals
AnimalsQuieter vibes for city spiders
How much a web vibrates affects how well a spider senses when that web has captured prey. But webs attached to concrete, plastic and other artificial materials vibrate less than do those built on natural materials, such as twigs or leaves.