The Violent Side of Video Games
Playing video games and watching TV and movies can change the way we act, think, and feel.

Kids can become quite emotional while playing video games, especially violent games.
Lipik1/iStock/Getty Images Plus
By Emily Sohn
Part 1 of 2: Video Games—Good or Bad?
Next week: What Video Games Can Teach Us
When I was a kid, I was obsessed with video games.
I saved my allowance to buy new games every month. I read Nintendo magazines for tips about solving the Super Mario Brothers adventures. I played so many hours of Tetris that I used to dream about little blocks falling perfectly into place.
There were physical effects, too. My thumbs turned into machines, quick and precise. During especially difficult levels of play, my palms would sweat. My heart would race. I’d have knots in my stomach from anxiety. It was the same feeling I’d sometimes get from watching scary movies or suspenseful TV shows.
 |
|
Playing video games can take over your life.
|
After a while, I started to think that looking at screens and playing games all the time might be affecting me in ways I didn’t even suspect. It turns out that I was probably right.
Scientists are discovering that playing video and computer games and watching TV and movies can change the way we act, think, and feel. Whether these changes are good or bad has become a subject of intense debate.
Concerns about violence
Violence is one of the biggest concerns, especially as computer graphics and special effects become more realistic. Some parents and teachers blame school shootings and other aggressive behavior on media violence—as seen in TV programs, movies, and video games.
“If you’ve ever watched young children watching kickboxing,” says child psychologist John Murray, “within a few minutes they start popping up and pushing and shoving and imitating the actions.” Murray is at Kansas State University in Manhattan, Kansas.
There’s also evidence that people become less sensitive to violence after a while, Murray says. In other words, you get so used to seeing it that you eventually think it’s not such a big deal.
Then there’s the “mean world syndrome.” If you watch lots of violence, you may start to think the world is a bad place. I still sometimes have trouble falling asleep if I watch the news on TV or read the newspaper right before going to bed.
Still, it’s hard to prove that violence on TV leads to violence in real life. It might be possible, for example, that people who are already aggressive for other reasons are more drawn to violent games and TV shows.
Brain clues
To try to make the link between seeing violence and acting violently, Murray is looking for clues in the brain.
In his most recent study, eight boys and girls between the ages of 8 and 12 watched a series of video clips. Some clips showed violent fighting scenes of Sylvester Stallone from the movie Rocky IV. Other clips were full of action, but no violence. Others were just blank screens.
During the experiment, each kid lay inside a special brain-imaging machine. Such a machine takes pictures of the brain and shows which parts of the brain are working at different times.
Murray and his colleagues found that exposure to violent video clips activated the amygdala, a thumbnail-sized area in the brain. The right side was particularly active.
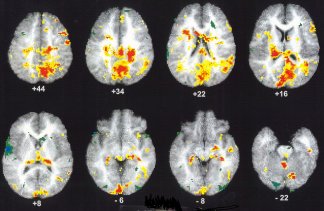 |
|
The colored parts of these images—each one a cross section of a brain—show which parts of the brain are active when children view a violent video clip but not when they view a nonviolent clip.
|
| John Murray, Kansas State University |
The amygdala is best known as the “fight or flight” organ. It senses danger and prepares you to either go to battle or run away. Your breathing slows down. You become hyper-aware of movements in the environment. And blood rushes to your brain’s core, among other effects.
“If someone drops a snake in front of you, most people . . . gasp,” Murray says. “That’s actually the amygdala responding.”
Video power
Most of the research has focused on TV and movie violence, mainly because TV and movies have been around much longer than video games, says psychologist Craig Anderson of Iowa State University in Ames, Iowa. Anderson has a Web site dedicated to looking at the link between video games and violence.
In his own research and in analyses of research by others, Anderson says that he has detected a connection between violent video games and violent behavior. He has found that people who repeatedly play violent games have aggressive thoughts and become less helpful and sociable. Physically, their heart rates accelerate.
Video games might have an even more powerful effect on the brain than TV does, Murray says. Players actively participate in the violence. In games like Grand Theft Auto 3, for example, the goal is to kill as many people as you can. The more violent you are, the more points you win.
Next time you play a violent video game, Murray suggests, check your pulse just before and after each round as one way to see how the game affects you.
“Ninety-nine percent of the time, I’ll bet your heart rate will have increased rather dramatically while playing one,” Murray says. “This indicates that . . . you are being affected.”
Three teenagers from Puerto Rico have data to back up that observation. At the International Science and Engineering Fair in Cleveland last year, Wildaliz Arias Perez, Derek Mercado Rivera, and Jacqueline Velez Gonzales presented a study looking at how video games affect people.
With the help of a school nurse, the high school seniors found that people of all ages showed a rise in blood pressure and heart rate after playing the superviolent game Capcom vs. SNK Pro. Playing Super Bust-A-Move 2, an active, nonviolent game, did not have the same effect.
Kids in Puerto Rico are addicted to video games just like in the United States, Derek told me, and he worries about the consequences. “So many kids have to play all day, like more than 4 hours,” he said.
Not so fast, some researchers say. Although violent video games increase a person’s heart rate and blood pressure, it doesn’t necessarily follow that such games make a person more violent. It might not be fair to blame all—or even a part—of society’s problems on media violence, these critics say.
And there’s more to video games than just violent content. In fact, a variety of studies are starting to show that playing video games can actually help people develop visual skills, learn about computers, and stay interested in school.
Next week: In part 2, read about some of the ways in which video games might actually help you out: What Video Games Can Teach Us.
Word Find: Video Games and Violence
Comments:
Yes, video games desensitize people, but so do movies and television shows. Blaming children being violent on games and such isn’t right. Parents who are too busy living their own lives to pay attention to their kids are to blame more than games, because that’s all they are—games. Soon, someone will say that playing cowboys and Indians, or playing with toy soldiers, is bad for young children.—Akemi, 22
I have been playing video games for a large majority of my life. I (as with many of my friends) do not like these violent video games because they are violent, but because they create a great form of competition between my friends and me.—Curtis, 17
I think that while, yes, video games may contribute to violence, there are many other factors for the kids to allow the violence to affect them.—Heather, 16
http://www.pbs.org/kcts/videogamerevolution/impact/myths.html: go there and read it.
Video games don’t cause violence, society does.—Bob, 16
OMG you were so wrong about GTA3. You only do what they tell you, you earn
money and pass missions. But I do admit that these games make me more violent!—Stacey, 14
People in the Middle Ages were chopping each other’s heads off and they didn’t have any TV. They didn’t play Mario.—Jhamal, 16
After reading this article, I too have to express my opinion in that the choices for the video games were bad choices in conducting this experiment! If you are looking for violent video games, try Doom 3, God of War, or Mortal Kombat. They have . . . blood and gore present and produce more of a challenge. Simply having stylized action fighting doesn’t necessarily make it violent.—Matt, 19
I’ve experienced a lot of violence during video games because of repetitiveness rather than the actual gore itself. I’m so used to [first person shooter] games that I can play the game, killing people, without any sort of violence whatsoever. . . . It’s when you repeat the game for 2 yrs. straight that short bursts of aggression are visible.—David, 15
After reading this article I have to say that, yes, video games do have MINOR side affects on people who play games. I have been playing games since the age of about 4. And I’m not a violent person. I have the entire Mortal Kombat
series for a majority of the platform game systems. And I beleive that the games you picked for your studies were bad choices. Capcom vs. SNK is not a violent game. There is no animated blood nor is there any gore in the game. Also the comment you made about GTA 3 was wrong as well. The object of the game is not to kill as many people as possible. The object of the game is to do what you’re told and you might have to kill a few people. Also the game is rated M for a reason. If parents buy their children these games then they should not be allowed to file lawsuits against the developers of these games.—Eric, 16
Going Deeper: