Animals
-
 Planets
PlanetsThe desert planet in ‘Dune’ is pretty realistic, scientists say
Humans could live on the fictional planet Arrakis from Dune. But thankfully giant sandworms probably could not.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSee how hummingbirds sneak through small spaces
Anna’s hummingbirds can use a couple of different techniques to get through gaps smaller than their wingspan.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists Say: Compound Eye
Compound eyes made up of many smaller visual structures may not produce crisp images, but they offer a great field of view.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSurprise! These animals can help fight climate change
Some animals help fight climate change by boosting the amount of carbon dioxide that plants, algae and bacteria absorb from the atmosphere.
-
 Brain
BrainHerbal medicine could help recovery after concussion
A finalist at Regeneron ISEF found that a plant native to China could supplement a common pain reliever that comes with unwanted side effects.
-
 Animals
AnimalsElusive worm-lizards sport weird, spooky skulls
CT scans of these mysterious creatures turned up bizarre internal features. They could offer clues about amphisbaenians’ largely unknown behavior.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDancing spiders inspired this biologist to teach others
Inspired by his research in animal communication, Echeverri began exploring ways to teach others about science while finishing his Ph.D. Today, he shares his passion for spiders as a science communicator.
-
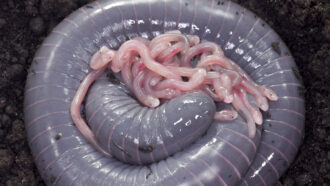 Animals
AnimalsThis egg-laying amphibian feeds its babies ‘milk’
Similar to mammals, this caecilian — an egg-laying amphibian — makes a nutrient-rich, milk-like fluid to feed its babies up to six times a day.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsAmong mammals, males aren’t usually bigger than females
In a study of more than 400 mammal species, less than half have males that are heavier than females.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLet’s learn about animals’ bizarre sleep schedules
From reindeer that snooze while chewing to penguins that take thousands of naps each day, the animal kingdom has some truly weird sleep patterns.
-
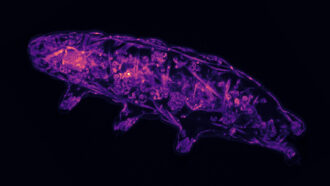 Animals
AnimalsTardigrades survive harsh conditions by almost dying. Here’s how
Under stress, a chemical change signals these water bears to switch between live and mostly dead.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLet’s learn about Godzilla and King Kong
These blockbuster monsters are too big to exist. But if they were real, what adaptations would each bring to battle?