Brain
-
 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Receptor
This molecule is a chemical messenger’s docking station. A receptor serves as a lock for cell activity.
-
 Brain
BrainCool Jobs: Decoding how your brain ‘reads’
For some stroke victims and people with dyslexia, reading is nearly impossible. These researchers are working to understand why.
-
 Space
SpaceEn route to Mars, astronauts may face big health risks
Going into space brings the thrill of a new frontier — and risks that scientists are racing to understand, from radiation to isolation.
-
 Brain
BrainWoodpecker brains host protein linked with human brain damage
Woodpeckers peck with a force great enough to give people concussions. Now a study shows that birds, too, may suffer some brain damage.
-
 Brain
BrainUnlike adults, teens don’t perform better when the stakes are high
Adults tend to do better on tasks that have bigger rewards. Not teens. This difference might have to do with the rewiring of the brain during adolescence, new data suggest.
-
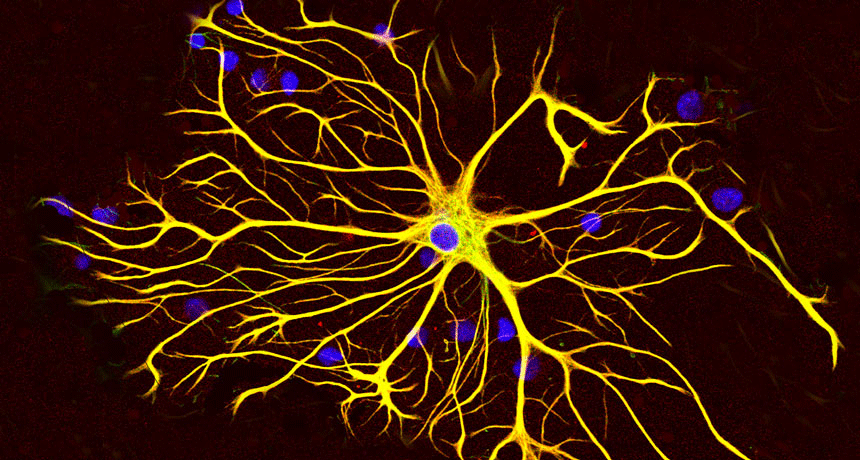 Brain
BrainOw! These cells might help brains remember pain and fear
The brain may learn from traumatic experiences with the help of special cells, a new study finds. Scientists used to think these cells, called astrocytes, were just there to support others.
-
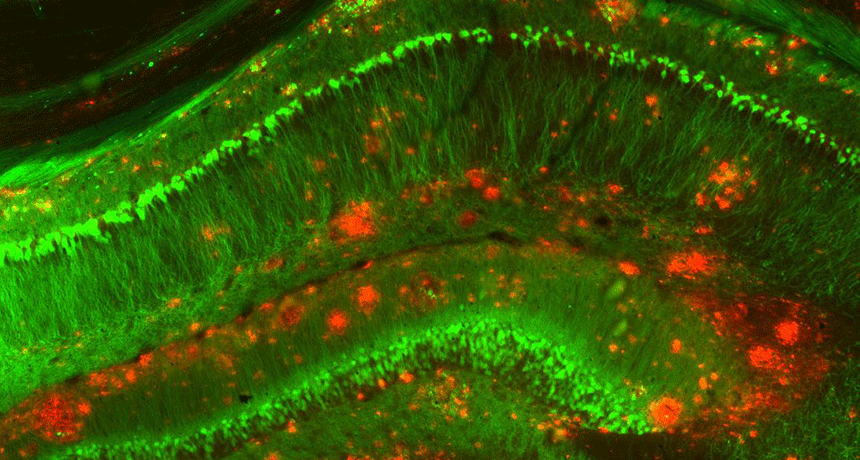 Brain
BrainAlzheimer’s protein can sneak into the brain from the blood
Experiments in mice show that proteins linked with Alzheimer’s disease can enter the brain from the blood, then stockpile there.
-
 Brain
BrainTrading smartphone time for sleep? Your loss
A new study shows more and more teenagers are hanging out on devices when they should be catching ZZZs, putting their health at risk.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSmall genetic accident made Zika more dangerous
A new study finds that a tiny mutation made the Zika virus more dangerous, by helping it kill cells in the fetal brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnalyze This: Does moderate screen time boost teen happiness?
Computers, smartphones and TVs are everywhere. And scientists are trying to discover whether that’s a good thing for our well-being.
-
 Brain
BrainA cell hookup helps the tongue tell sweet from sour
To keep your sense of taste, new taste cells need to hook up to your brain every few weeks. Now, scientists have figured out how they do it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Rabies
Rabies is a disease caused by the rabies virus. There is a vaccine, but without it, people and animals can die from this disease.