Brain
-
 Brain
BrainMistakes: A key to learning
This man uses a robotic arm to move a cursor across a computer screen. The screen blocks his view of his hand and arm. This focuses his attention on any errors he makes as he tries to move a cursor to a target location.
-
 Brain
BrainLearning rewires the brain
Brain cells actually change shape as we learn. It’s one way we cement new knowledge. And much of the action happens as we sleep.
-
 Brain
BrainLacrosse: Different genders, same injuries
Scientists find that boys’ and girls’ versions of lacrosse lead to similar injuries. Because girls frequently get concussions, the study argues that like the boys, girls too should wear helmets.
-
 Brain
BrainChoosing shocks over contemplation
Some people think being alone is unpleasant. In one new study, some found choosing to get a painful shock helped them endure being alone for 15 minutes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBugs may have made us brainy
Finding and eating bugs when other food was scarce helped primates — including our ancestors — evolve bigger and better brains. At least that’s the conclusion of a new study in Costa Rica.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung blood: The elixir of youth?
Old mice show improved memory when blood from young mice circulated through their brains, a new study finds. Other studies suggest one ingredient in that young blood might be all it takes to deliver benefits.
-
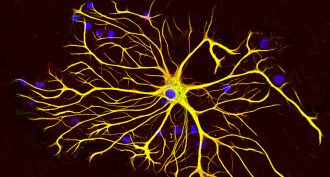 Brain
BrainHunger’s little helpers
Astrocytes were thought to be nothing more than support cells for neighboring nerve cells. A new study suggests they do much more. These brain cells may help control appetite, too.
-
 Brain
BrainFootball hits the brain hard
The brain’s hippocampus helps store memories. It is smaller in college football players — especially if they have suffered concussions.
-
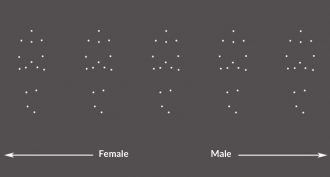 Brain
BrainThe scent of a woman — or a man
Animals unwittingly signal things about themselves by giving off subtle scents. A new study claims the same is true for people.
-
 Brain
BrainGhosts in your head
Many people see, feel and hear things that aren’t really there — despite how much their brain tries to convince them otherwise.
By Kirsten Weir -
 Brain
BrainLoneliness can breed disease
Everyone experiences loneliness from time to time. But when allowed to persist, loneliness can damage your health and steal years from your life.
By Hugh Westrup -
 Brain
BrainGetting a head start on autism
Early diagnosis followed by early treatment may reduce autism’s impact on kids — and help them to communicate better.
By Bryn Nelson