Chemistry
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: The bacteria behind your B.O.
Special glands in our armpits give us our signature stink. But it’s not our sweat that’s to blame. It’s the bacteria that gobble it up.
-
 Tech
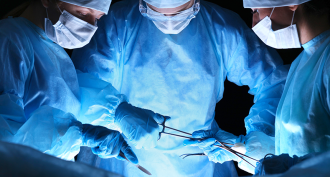
TechA new electric surgery tool may someday fix nose, ear and eye problems
A new surgery tool uses electricity to reshape ear and nose tissue in minutes, without pain. Someday, it might even work on eyes to restore normal vision.
-
 Physics
PhysicsTiny new magnets are not only squishy but also liquid
Researchers have just created liquid droplets that behave like tiny bar magnets. The movement of these external magnets might help control robots and more.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFireworks shower the skies with science
Filling the night sky with fireworks requires the help of chemists, electrical engineers and people who can choreograph theatrical shows.
By Sid Perkins -
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Ferrofluid
Ferrofluids are liquids with tiny magnetic particles in them. These liquids respond to magnets.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesSlimy fish could aid the search for new drugs
Fish slime could teach scientists about bacteria that live on fish and aid in the hunt for new kinds of antibiotics.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentStudies show how homes can pollute indoor air
Cooking, cleaning, applying makeup or deodorant and other activities may sometimes leave indoor air as polluted — or worse — than outdoor air, new research suggests.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryRemote-controlled nanoparticles could fight cancer — gently
A new type of nanoparticle would keep toxic cancer drugs wrapped up so they won’t poison healthy cells. But a remote signal can unleash this cancer-killing medicine once it reaches a tumor.
-
 Physics
PhysicsScientists now know why microwaved grapes make plasma fireballs
Grapes trap microwave energy that bounces back and forth within the fruit. Until boom — a plasma!
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryShape-shifting chemical is key to new solar battery
Storing solar energy is a challenge. A new, shape-shifting molecule may provide a solution.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySmartphone app helps researchers track art ‘acne’
Metal soaps can form damaging blisters on the surface of oil paintings. Scientists are tracking these “breakouts” to protect priceless art.
By Jeremy Rehm -
 Chemistry
ChemistryHam bone broth could be a tonic for the heart
Health and fitness websites claim that drinking bone broth is a miracle cure. Here’s what some new research has to say about that.