Chemistry

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCan concrete conquer air pollution?
Powdered concrete could remove the sulfur dioxide and other pollutants that are spewed into the air when electric-power plants burn fossil fuels, a lab study suggests.
By Sid Perkins -
 Tech
TechCool Jobs: Bringing you summer thrills
Fireworks and ride designers combine math and science to engineer some frightfully good summer fun.
By Gerri Miller -
 Chemistry
ChemistryNew ‘magnet’ pulls pesky nonstick pollutants from drinking water
Chemicals that help make pans nonstick can themselves stick around forever in the environment. But a new material can remove them from drinking water.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Photochromic
Photochromic chemicals change shape when exposed to a specific wavelength of light. The shape change changes the chemical’s color.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Catalyst
Sometimes a chemical reaction can take a while. If speed is needed, a catalyst can help.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTrees can make summer ozone levels much worse
The greenery can release chemicals into the air that react with combustion pollutants to make ozone. And trees release more of those chemicals where it gets really hot, a new study finds.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesWorld’s deepest zoo harbors clues to extraterrestrial life
Scientists have found a wide range of life deep below Earth’s surface. The discoveries could help inform our search for life on other planets.
-
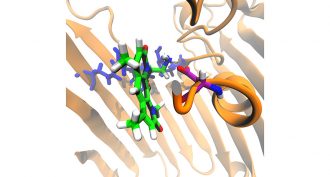 Chemistry
ChemistryNew rules point scientists toward next-gen germ-killers
Shape and other features help germ-killing drugs make it through barriers to enter bacteria. Knowing how they do this could lead to more and better better antibiotics.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryTo test pill coatings, try a stomach in a flask
Which pain reliever should you buy? The tablet, gel tab or compressed caplet? A teen did an experiment to find out.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryBPA-free plastic may host BPA-like chemical, teen finds
Something has to replace the BPA in ‘BPA-free’ plastics. A teen has been probing what that is.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryCool Jobs: Counting calories
Do calories count? A nutrition label doesn’t tell the whole story. Meet three researchers working to shed light on the complex connections between food and health.
-
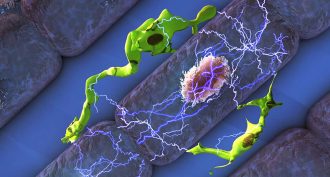 Chemistry
ChemistrySteady heartbeats may depend on white blood cells
Biologists have just found a new role for germ-fighting white blood cells. In the heart they appear to serve as pacemakers so that the heart beats regularly.