Chemistry

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Earth
EarthBeyond diamonds: Search is on for rare carbon crystals
A search for previously undiscovered carbon minerals was announced in December 2015. Researchers have begun finding a handful and are actively scouting for dozens more.
By Sid Perkins -
 Chemistry
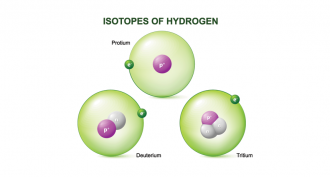
ChemistryScientists Say: Isotope
An isotope is a variety of an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons — or neutrally charged particles.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists know that you pee in the pool
A new way to find urine in pools and hot tubs measures the concentration of an artificial sweetener in the water.
By Sid Perkins -
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Atomic number
How do you know where an element sits in the periodic table? Count its protons to get its atomic number.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDid your burger come with a side of non-degrading pollutants?
Perfluorinated compounds pollute the environment and might harm human health. A new study shows that one place they often show up is the paper and cardboard used to package fast foods.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExplainer: What is a catalyst?
Catalysts are used in manufacturing and many technologies. They’re also found in living things. They help chemical reactions move along.
-
 Chemistry
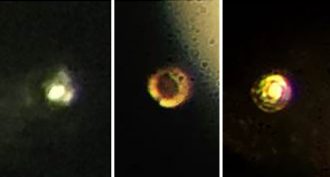
ChemistryScientists claim to have turned hydrogen into a metal
Most people know hydrogen as a gas. But under high pressure, scientists now think they’ve converted it into a reflective metal. Not everyone is convinced.
-
 Tech
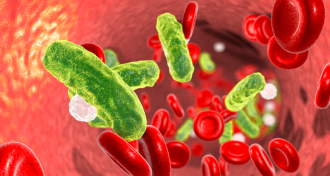
TechMagnets may one day cull deadly germs from blood
A new technique for slowing the deadly condition called sepsis would use tiny iron particles and magnets.
By Sid Perkins -
 Tech
TechHow to spin synthetic spider silk
A new method for spinning artificial spider silk combines parts of proteins from two species and mimics what happens in a spider’s silk-forming gland.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHere’s how hot water might freeze faster than cold
There’s a new explanation for how hot water freezes faster than cold water. But not everyone agrees it’s right, or that the effect can happen at all.
-
 Tech
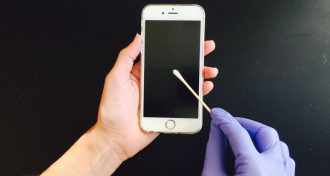
TechFingers leave tell-tale clues about you on your phone
Analyzing chemicals on a cell phone tells researchers what the caller had been up to. That includes recent meals and where they'd been.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Sublimation
Matter doesn’t always go from solid to liquid to gas. Sometimes it skips a step.