Chemistry

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Chemistry
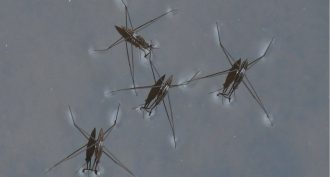
ChemistryScientists Say: Surface tension
Surface tension is what makes water in your glass seem like it’s covered by an invisible membrane holding it together.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMilking chocolate for its health benefits
Researchers figure out how to give milk chocolate the same health benefits as dark chocolate. The secret ingredient is an extract from peanut skin.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryScientists Say: Unsaturated fat
These fats are found in foods like olive oil. It’s their special bonds that make them go with the flow.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryNew coating for metals could cut engine wear
Scientists have developed a new coating for engine parts that could reduce friction and engine wear. One big benefit: Cars may require fewer oil changes.
By Sid Perkins -
 Chemistry
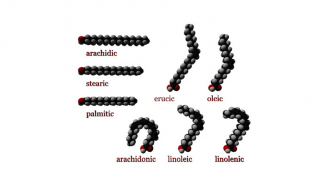
ChemistryScientists Say: Fatty acid
Fats are important, especially fatty acids. These molecules serve many purposes, but they are all constructed the same way.
-
 Chemistry
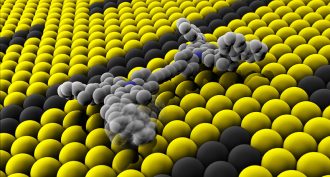
ChemistryChemistry Nobel honors pioneers of world’s smallest machines
Three chemists are being honored with a Nobel Prize for their pioneering work creating itty bitty machines, including a microscopic ‘nanocar.’
By Tina Hesman Saey and Thomas Sumner -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy trans fats became a food villain
Trans fats are now known as a dietary villain. But in the beginning, scientists thought they were better than butter.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentLaundering clothes may send indoor pollutants outdoors
Clothing absorbs pollutants from indoor air. During washing and drying, the fabric releases those chemicals into the outdoor environment, a new study finds.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChanging the world with chemistry
What does a scientist look like? Meet these amazing women in chemistry.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryLab creates new, unexpected type of ‘firenadoes’
A newly discovered type of fiery vortex burns hot and generates little soot. Scientists suspect it could be a solution to cleaning up oil spills at sea.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
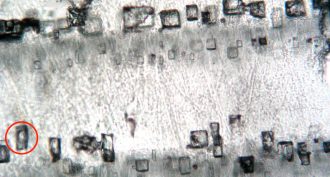
EarthOxygen-rich air emerged super early, new data show
Scientists had thought animals were slow to emerge because they would have needed oxygen-rich air to breathe. A new study finds that plentiful oxygen may have developed early. So animals may have been late on the scene for another reason.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryGot milk? Roach milk could be a new superfood
Scientists have just figured out the recipe for cockroach milk. And that could be a first step toward making it part of the human diet. Yum!
By Dinsa Sachan