Earth
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemists look to mine silver from laundry wastewater
Recovering silver from wastewater could prevent the metal from ending up in lakes, rivers and the ocean, where it could poison wildlife.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change threatens future Winter Olympics
Higher temperatures, less snow mean many former Winter Olympics sites soon will no longer qualify to host future games, concludes a new analysis.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureHow to grow a cacao tree in a hurry
Chocolate is made from the pods of the cacao tree. To reproduce this plant quickly for research, scientists use clones.
-
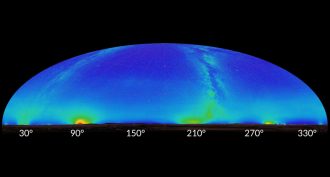 Earth
EarthPollution from new technologies threatens astronomy
Pollution from new technologies will make it harder to observe the night sky, astronomers say.
By Dan Garisto -
 Agriculture
AgricultureRobots will control everything you eat
Robots are now being introduced into all phases of how food is grown and prepared. In the future, though, they will be common.
By Terena Bell -
 Climate
ClimateA meteor explodes over Michigan
Here’s how scientists tracked down the source of a heavenly explosion over rural Michigan, last week.
-
 Physics
PhysicsExplainer: Winds and where they come from
Temperature and pressure are critical factors affecting why the wind blows where it does. Understanding the nature of wind can teach us a lot about weather.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryChanging toothpastes? Change your toothbrush
Scientists have found that toothbrush bristles absorb triclosan, then release the potentially toxic chemical when users switch toothpastes.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists at last link some extreme weather to human activities
Scientists say that research shows several of 2016’s extreme weather events would never have happened without the help of human-caused climate change.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEscaping narwhals can freeze and flee at the same time
Narwhals’ heart rates plummet while diving quickly to get away from people. The combination may stress the whales as human activity increases in the Arctic.
-
 Earth
EarthWater waves can have literally seismic impacts
Certain types of seismic waves are generated by waves on large lakes. These ground waves could be used to map fault zones or to monitor ice cover in polar lakes.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthExplainer: Seismic waves come in different ‘flavors’
Earthquakes generate several different types of seismic waves, some more damaging than others
By Sid Perkins