Earth
-
 Earth
EarthMornings become electric
Lightning packs a wallop in the morning. The most powerful lightning strikes in the continental United States usually peak before noon.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking wastes may be toxic, tests show
Fracking operations have been polluting the environment. Some wastes have hormonal effects. Studies in mice now show that prenatal exposures to these wastes can trigger subtle but disturbing organ impacts.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistryCooking up life for the first time
The basic components for life could have emerged together nearly 4 billion years ago on the surface of Earth, chemists report.
By Beth Mole -
 Microbes
MicrobesLife’s ultra-slow lane is deep beneath the sea
Biologists had suspected the deep seafloor would be little more than barren sediment. But they found a surprising amount of oxygen — and life.
By Beth Geiger -
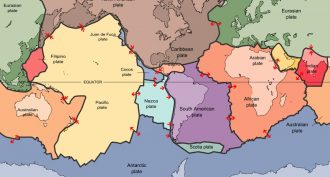 Earth
EarthExplainer: Understanding plate tectonics
Plate tectonics is the process whereby Earth continually rebuilds itself — and causes destructive events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
-
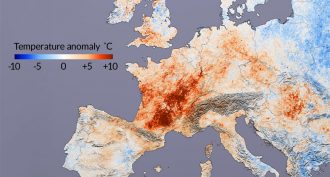 Environment
EnvironmentArctic warming bolsters summer heat
Rapid warming in the Arctic is sapping summer storms of their power to cool. That worsens heat waves across the Northern Hemisphere.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFinding out why birds are out of range
Sometimes people see large numbers of birds outside of their normal range. A student examined how to predict these excursions.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentCorals dine on microplastics
Plastic in the ocean is a growing problem. New research finds that corals may eat tiny bits of plastic, prompting new concerns about the health of living reefs.
-
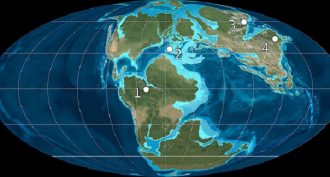 Earth
EarthAncient ocean linked to supercontinent’s breakup
The supercontinent Pangaea started breaking apart 200 million years ago. This may have been triggered by the shrinking of the Tethys Ocean, a new study finds.
-
 Earth
EarthNews Brief: Volcanic spark zaps ash to glass
The lightning associated with some erupting volcanoes can be quite crafty — turning ash into lots of microscopic glass beads.
-
 Climate
ClimateBuildings may be chasing L.A.’s fog away
Roads and buildings that have mushroomed up around Los Angeles in the past half-century. Now, a study finds they may have created conditions that limit fog. And that could further dry out this very arid part of America’s West Coast.
-
 Climate
ClimateScientists confirm ‘greenhouse’ effect of human’s CO2
Government scientists link directly, for the first time, a boost in warming at Earth’s surface to increasing levels of carbon dioxide. Much of that gas has been released by human activities, such as coal burning and gas-burning vehicles.