Environment
-
 Climate
ClimateStudent scientists work to help all of us survive a warmer world
From glaciers in the refrigerator to a rover in the field, here’s how young scientists are looking to help us adapt to climate change.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentWashing your jeans too much might pose risks to the environment
Jeans shed thousands of denim fibers in every wash. Those fibers, and the chemicals used to treat them, now are showing up in even the Arctic Ocean.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsScientists Say: Desert
Deserts are ecosystems that get less than 250 millimeters (10 inches) of precipitation per year.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHow to recycle ‘nonrecyclable’ plastics
A new process can convert some nonrecyclable plastics into a type that now can be reused. That could greatly cut down on wastes sent to landfills.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAnalyze This: Perfumes from everyday products collect in distant ice
Common scent-bearing chemicals are trapped in ice cored from Europe’s tallest peak. Dig into the data to find a story behind that pollution.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhale blowholes don’t keep out seawater
Whales’ blowholes aren’t as protective as scientists had thought. They not only can let in water but also pollutants.
By Rasha Aridi -
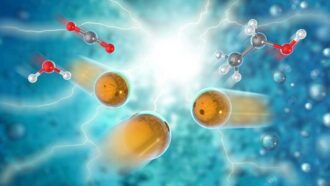 Chemistry
ChemistryNew solution for carbon dioxide: Turn it into ‘green’ fuel
Chemists have created a new way to convert carbon dioxide into ethanol. It might one day help remove excess CO2 — a greenhouse gas — from the air.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA single chemical may draw lonely locusts into a hungry swarm
Swarms of locusts can destroy crops. Scientists have discovered a chemical that might make locusts come together in huge hungry swarms.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentBusy beavers may be speeding thaw of Arctic permafrost
As climate change continues, busy beavers are expanding their range in Alaska. Their dams could further speed the loss of permafrost there and promote local warming.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDust can infect animals with flu, raising coronavirus concerns
Dust particles kicked up from some virus-contaminated surface can become a source of new infections, rodent data show.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPesticides contaminate most food of western U.S. monarchs
Monarch caterpillars eat only milkweeds. A new study finds widespread pesticide use has tainted these plants across the insect’s western U.S. breeding grounds.
-
 Space
SpaceScientists Say: Solar
What do solar energy, the solar year and solar flares have in common? They’re all related to the sun.