Genetics
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists Say: Loci
The DNA in our bodies contains thousands of genes, all with different functions. We use a special word for their location.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsScientists Say: Allele
What makes your eyes green or brown? Different versions of the same gene. We call these alternative forms by a separate name.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in ivory pinpoints elephant poaching hot spots
Thousands of elephants have been killed for their ivory tusks. A new study used DNA in ivory to trace where most of the killings happen.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew ways to fight the flu
Influenza sickens millions each year. A worldwide epidemic could kill many of them. Fortunately, new ways to fight the flu offer hope — before it’s too late.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA germ stopper for blood products
A new system can disable almost all viruses or bacteria that are lurking in donated blood platelets and plasma.
By Tara Haelle -
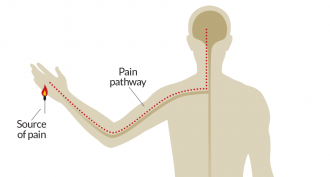 Genetics
GeneticsAltered gene leaves people totally painfree
That’s not a good thing for these people. Still, it could lead to a new class of drugs to help people who now suffer from chronic pain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCatching ZZZs may retrieve lost memories
Forgetful? Maybe you’ve forgotten to get enough shuteye. A study in fruit flies suggests that a good sleep can boost their ability to remember things.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDo mosquitoes love you? Blame your parents
By studying twins, scientists found that how attractive we are to mosquitoes depends partly on our genes. That could lead to better bug repellents.
-
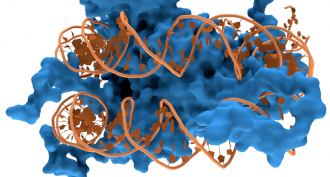 Life
LifeHow DNA is like a yo-yo
When not in use, DNA coils tightly. But it must uncoil for the cell to ‘read’ its genes. Physical forces affect how easily that happens, new data show.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSilencing genes — to understand them
Hijacking a cell process called RNA interference can let scientists turn off a selected gene. Its silencing can point to what genes do when they’re on — and may lead to new treatments for disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPenguins? How tasteless
Penguins may look all dressed up in tuxedo-wear, but their taste buds are the bare minimum. This means that the birds will never sense more than a hint of their meals’ true flavors.
-
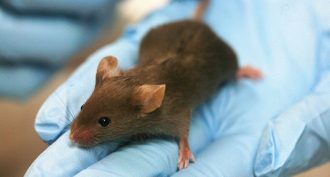 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMice can teach us about human disease
Humans and mice look and act very differently. But 85 to 90 percent of their genes are the same or quite similar. So an international group of scientists is deciphering the instructions in mouse genes to help us better understand our own.