Genetics
-
 Animals
AnimalsA dog’s breed doesn’t say much about its behavior
Many people associate dog breeds with specific behavioral traits. But breed appears to account for only about 9 percent of behavioral differences.
By Anna Gibbs -
 Animals
AnimalsLosing some genes may explain how vampire bats can live on blood
Loss of 13 genes active in other bats could support the vampires’ blood-eating strategies and adaptations.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInfected caterpillars become zombies that climb to their deaths
By tampering with genes involved in vision, a virus can send caterpillars on a doomed quest for sunlight.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsSurprise! Sixteen tiny wasp species found masquerading as one
Scientists used new and old tools to overturn 160-year-old ideas about this wasp. They show you can’t tell a wasp by its looks.
-
 Health & Medicine
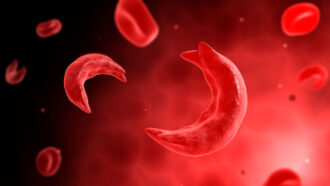
Health & MedicineSickle-cell gene therapies offer hope — and challenges
Doctor Erica Esrick discusses existing treatments and an ongoing clinical trial for a gene therapy to treat sickle cell disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
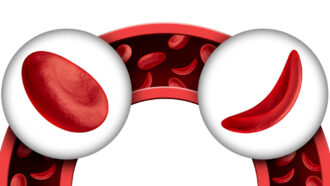
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is sickle cell disease?
Gene mutations can alter an individual’s hemoglobin in ways that curl their blood cells. This can cause painful sickle cell disease.
By Erin Garcia de Jesús and Janet Raloff -
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in air can help ID unseen animals nearby
Analyzing these genetic residues in air offers a new way to study animals. It could give scientists a chance to monitor rare or hard to find animals.
By Laura Allen -
 Animals
AnimalsMeat-eating bees have something in common with vultures
Flesh-eating bees have acid-producing gut bacteria, much as vultures do. It lets them safely snack on rotting meat.
-
 Humans
HumansGenetics show humans likely trace back to Africa
Our history began looking ever more complex once geneticists revealed our ancestors picked up new DNA as they traveled across time and continents.
By Erin Wayman -
 Genetics
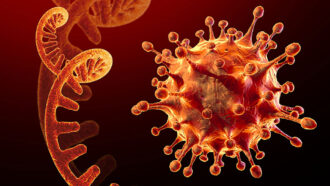
GeneticsExplainer: What is RNA?
A partner to DNA, cells use this molecule to translate the instructions for making all of the many proteins that your body needs to function.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWill the woolly mammoth return?
Scientists are using genetic engineering and cloning to try to bring back extinct species or save endangered ones. Here’s how and why.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCloning boosts endangered black-footed ferrets
A cloned ferret named Elizabeth Ann brings genetic diversity to a species that nearly went extinct in the 1980s.