Health & Medicine
-
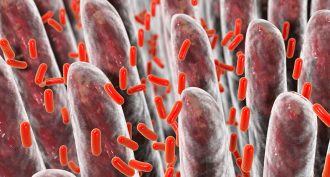 Microbes
MicrobesGut bacteria may affect how well your medicines work
Gut bacteria can chemically change the drugs people swallow. ID-ing a patient’s microbes might one day help doctors prescribe the most effective drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBy the numbers: How infectious measles and other diseases spread
A number called R0 measures how contagious an infectious disease is. It helps explain why measles is so dangerous.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Obesogens
The chemicals can change how the body stores fat or how often someone feels hungry — increasing the risk for obesity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBats are now the primary source of U.S. rabies deaths
Although human rabies is not common in the United States, it still occurs. But here dogs are no longer the likely source of this oft-lethal infection: Bats are.
-
 Earth
EarthAntibiotics pollute many of the world’s rivers
A survey of 165 rivers finds unsafe levels of antibiotics at one in six sites tested. Such pollution can leave germs resistant (unharmed) by the drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFighting spider-fear with a little Spider-Man
Many people are afraid of spiders or ants. Watching a movie clip with the critters in it might help make people more comfortable with them, a new study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYouthful rebellion leads some teens to eat better
Once 8th graders learned how food advertisements have been developed to influence them, many rebelled — and started eating healthier.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew risk from too much screentime
Americans of all ages are sitting more, according to a new national survey. And health experts find that worrisome.
By Mary Bates -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Myopia
Myopia is nearsightedness, where people have trouble seeing far away objects. This happens if someone’s eyes are slightly oval, instead of perfect spheres.
-
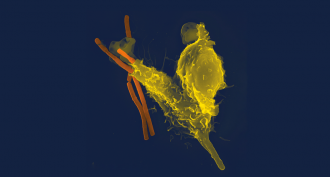 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Neutrophil
Neutrophils are the first cells to arrive when an infection takes hold. They can trap, eat and spew out chemicals that fight bad bacteria.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGeneticists get closer to knowing how mosquitoes sniff out our sweat
Scientists have found that a protein in the antennae of some mosquitoes detects a chemical in human sweat.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSea urchins inspired a strong new medical staple
Teens combined forces to study how a sea urchin spine might inspire a better medical staple.