Humans
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow sunshine may make boys feel hungrier
Males eat more on long summer days, but females do not. Hormones may explain this difference.
-
 Humans
HumansWhat does charred ancient poop reveal about early animal-raising?
Evidence from the dung may push the onset of animal raising back 2,000 years earlier than previously thought.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsFor some kids, their rock-star hair comes naturally
A variant of a gene involved in hair-shaft formation was linked to most of the uncombable-hair-syndrome cases analyzed in a recent study.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExamining Neandertal and Denisovan DNA wins a 2022 Nobel Prize
Svante Pääbo figured out how to examine the genetic material from these hominid ‘cousins’ of modern humans.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Aimee Cunningham -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyRats can chronicle human history
Rats have lived alongside people for thousands of years. Now, scientists can study the rats and their leavings to learn more about ourselves.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDogs and other animals could aid the spread of monkeypox
Now that monkeypox has spread to a dog, researchers fear other species could help the virus become widespread outside of Africa for the first time.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is mpox (formerly monkeypox)?
Once rare, the viral disease monkeypox exploded onto the global scene for the first time in 2022.
By Tina Hesman Saey and Janet Raloff -
 Psychology
PsychologyPersuasion can be used to change hearts and minds
Persuasion can be used for good — or ill — to change how people feel. To protect yourself against undue persuasion, pay attention.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryRecipes for modern beauty products aren’t so modern after all
An art historian has combined forces with chemists to uncover the science behind cosmetics used about 500 years ago.
-
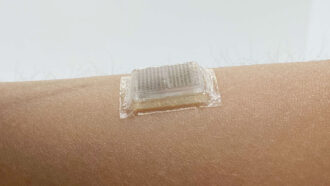 Tech
TechNew stick-on ‘sonar’ device lets you watch your own heart beat
This wearable patch might one day make personalized medicine affordable almost anywhere in the world.
By Asa Stahl -
 Climate
ClimateHeat waves appear more life-threatening than scientists once thought
This is bad news as a warming planet leads to growing numbers of excessive heat waves — and millions more people facing potentially deadly temperatures.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWildfire smoke seems to pose its biggest health risk to kids
New studies, some of them in young monkeys, point to vulnerabilities affecting kids' airways, brains and immune systems.
By Megan Sever