Humans
-
 Psychology
PsychologySocial media doesn’t, by itself, make teens unhappy or anxious
Checking social media frequently doesn’t necessarily cause unhappiness, a new study finds. Sleep, exercise and cyberbullying are also key.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUltrasound might become a new way to manage diabetes
Ultrasound turns on production of the hormone insulin in mice. Someday, it might help maintain healthy blood-sugar levels in people who were recently diagnosed with diabetes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is ultrasound?
These sound waves, which fall above the range of human hearing, are important in medicine, medical imaging and more.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCool Jobs: Poop investigators
Far from just being waste, poop is loaded with clues to the health, biology and behavior of whatever body produced it.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Brain
BrainBrain ‘ripples’ appear just before you remember something
Nerve cells in the brain’s hippocampus, a key memory center, fire together a second or two before people begin to recall an image, data now show.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyScientists Say: Mummy
Mummies are dead bodies that don’t rot. They can form under natural conditions or because of chemicals that stop decay.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t snooze on getting enough sleep
Sleeping the right amount at night is good for mental and physical health. Ironically, napping isn’t always helpful.
-
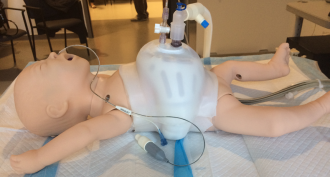 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTiny vest could help sick babies breathe easier
A new invention helps sick babies breathe easier. It looks like a tiny lifejacket and it avoids the mask and tubes that get in the way of breastfeeding.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCRISPR enters its first human trials
A host of new human trials are using a gene-editing tool known as CRISPR to treat genetic diseases — from sickle cell and cancers to a blinding eye disorder.
-
 Brain
BrainRoutine hits in a single football season may harm players’ brains
A group of college football players underwent brain scans after a season of play. The results suggest playing the sport could harm neural signaling.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOutbreak of lung disease, including 5 deaths, tied to e-cigarettes
Some 450 e-cig users have been hospitalized for severe lung disease across 33 states and U.S. territories. Five of them have died.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy links chemicals in ‘BPA-free’ plastics to obesity in kids
Scientists have linked exposure to chemicals found in BPA-free plastics and cans with obesity in kids and teens.