Humans
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyBeyond the El Paso shooting: Racist words and acts harm kids’ health
An author of a new report by the American Academy of Pediatrics describes how racist acts, such as gun violence, can lead to lifelong physical and mental harm
-
 Brain
BrainLasers make mice hallucinate
Scientists used a technique called optogenetics to make mice “see” vertical or horizontal lines that didn’t actually exist.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles can harm a child’s defense against other serious infections
Getting the measles can leave the body vulnerable to other infections months or even years later, scientists are finding.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome mama whales may whisper to keep calves safe from orcas
Even enormous whales can fear the threat that orcas pose to their babies. It now seems that some have taken to whispering to help their young stay off the killer whales’ radar.
-
 Brain
BrainHigh fat diet removes brain’s natural brake on overeating
At least in mice, high-fat diets promote overeating. And the problem appears to trace to changes that these foods make to cells in an appetite-control center within the brain.
-
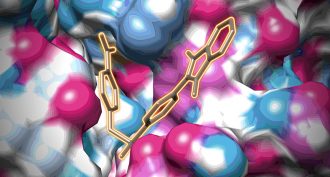 Microbes
MicrobesA surface crater in viruses may be key to keeping colds from spreading
A newly discovered pit on the surface of one family of viruses could help scientists fight the common cold and other infections.
-
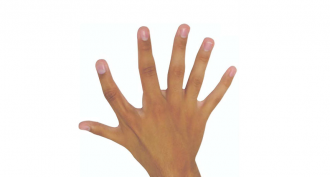 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA sixth finger can prove extra handy
Two people born with six fingers on each hand adeptly control their extra digits, using them to do tasks better than five-fingered hands.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA fungus plus a spider toxin equals a weapon to kill mosquitoes
A new weapon could help fight mosquitoes that spread malaria. It’s an engineered fungus that infects the insects — then kills them with a spider poison.
-
 Humans
HumansDNA reveals clues to the Siberian ancestors of the first Americans
Researchers discovered a previously unknown population of Ice Age people who crossed the Asia-North America land bridge.
By Bruce Bower -
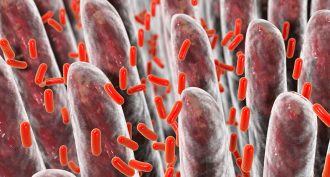 Microbes
MicrobesGut bacteria may affect how well your medicines work
Gut bacteria can chemically change the drugs people swallow. ID-ing a patient’s microbes might one day help doctors prescribe the most effective drugs.
-
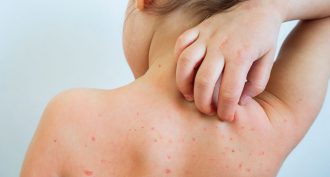 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBy the numbers: How infectious measles and other diseases spread
A number called R0 measures how contagious an infectious disease is. It helps explain why measles is so dangerous.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Obesogens
The chemicals can change how the body stores fat or how often someone feels hungry — increasing the risk for obesity.