Humans
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyScientists Say: Mummy
Mummies are dead bodies that don’t rot. They can form under natural conditions or because of chemicals that stop decay.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDon’t snooze on getting enough sleep
Sleeping the right amount at night is good for mental and physical health. Ironically, napping isn’t always helpful.
-
 Health & Medicine
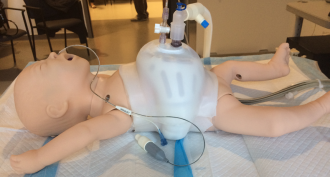
Health & MedicineTiny vest could help sick babies breathe easier
A new invention helps sick babies breathe easier. It looks like a tiny lifejacket and it avoids the mask and tubes that get in the way of breastfeeding.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCRISPR enters its first human trials
A host of new human trials are using a gene-editing tool known as CRISPR to treat genetic diseases — from sickle cell and cancers to a blinding eye disorder.
-
 Brain
BrainRoutine hits in a single football season may harm players’ brains
A group of college football players underwent brain scans after a season of play. The results suggest playing the sport could harm neural signaling.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOutbreak of lung disease, including 5 deaths, tied to e-cigarettes
Some 450 e-cig users have been hospitalized for severe lung disease across 33 states and U.S. territories. Five of them have died.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy links chemicals in ‘BPA-free’ plastics to obesity in kids
Scientists have linked exposure to chemicals found in BPA-free plastics and cans with obesity in kids and teens.
-
 Health & Medicine
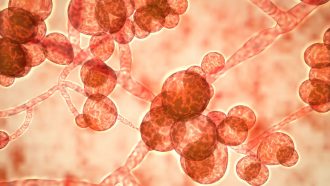
Health & MedicineClimate change may be aiding a deadly fungus in infecting humans
A deadly fungus infecting humans around the world may have been worsened by climate change.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists investigate suicide risk among LGBTQ+ teens
LGBTQ+ youths face higher suicide risks because of how society treats them as members of minority groups. But resources are available. And all teens can help.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRise in suicides emphasizes need to help teens deal with despair
Suicides are on the rise among U.S. adolescents and young adults. These data emphasize why people should reach out to friends who might have trouble coping with intense stress.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaping may have landed eight teens in the hospital
E-cigarette use can harm the lungs. Eight Wisconsin teens who developed severe lung injuries after vaping may be the latest victims.
-
 Earth
EarthAmericans consume some 70,000 microplastic particles a year
The average American consumes more than 70,000 microplastic particles a year. Scientists hope this estimate will spur others to look at health risks.