Humans
-
 Microbes
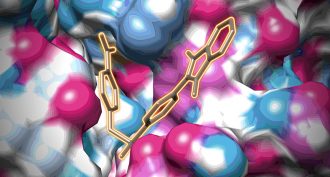
MicrobesA surface crater in viruses may be key to keeping colds from spreading
A newly discovered pit on the surface of one family of viruses could help scientists fight the common cold and other infections.
-
 Health & Medicine
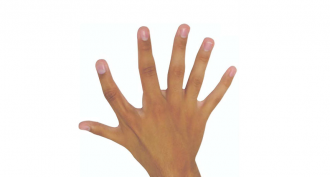
Health & MedicineA sixth finger can prove extra handy
Two people born with six fingers on each hand adeptly control their extra digits, using them to do tasks better than five-fingered hands.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA fungus plus a spider toxin equals a weapon to kill mosquitoes
A new weapon could help fight mosquitoes that spread malaria. It’s an engineered fungus that infects the insects — then kills them with a spider poison.
-
 Humans
HumansDNA reveals clues to the Siberian ancestors of the first Americans
Researchers discovered a previously unknown population of Ice Age people who crossed the Asia-North America land bridge.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
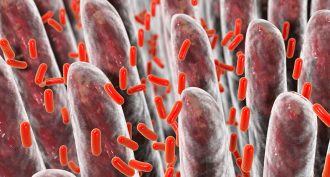
MicrobesGut bacteria may affect how well your medicines work
Gut bacteria can chemically change the drugs people swallow. ID-ing a patient’s microbes might one day help doctors prescribe the most effective drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBy the numbers: How infectious measles and other diseases spread
A number called R0 measures how contagious an infectious disease is. It helps explain why measles is so dangerous.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Obesogens
The chemicals can change how the body stores fat or how often someone feels hungry — increasing the risk for obesity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBats are now the primary source of U.S. rabies deaths
Although human rabies is not common in the United States, it still occurs. But here dogs are no longer the likely source of this oft-lethal infection: Bats are.
-
 Earth
EarthAntibiotics pollute many of the world’s rivers
A survey of 165 rivers finds unsafe levels of antibiotics at one in six sites tested. Such pollution can leave germs resistant (unharmed) by the drugs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFighting spider-fear with a little Spider-Man
Many people are afraid of spiders or ants. Watching a movie clip with the critters in it might help make people more comfortable with them, a new study shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYouthful rebellion leads some teens to eat better
Once 8th graders learned how food advertisements have been developed to influence them, many rebelled — and started eating healthier.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew risk from too much screentime
Americans of all ages are sitting more, according to a new national survey. And health experts find that worrisome.
By Mary Bates