Humans
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySchool bullying has risen in areas that supported Trump
Bullying rose in areas that favored Republican Donald Trump in the 2016 election for U.S. president. The new findings come from surveys of Virginia middle school students.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSnot Science: Stopping the sneeze
In my previous study, I compared thick and thin snot. Now, I’ll find out if a tissue makes a difference in how far a sneeze spreads.
-
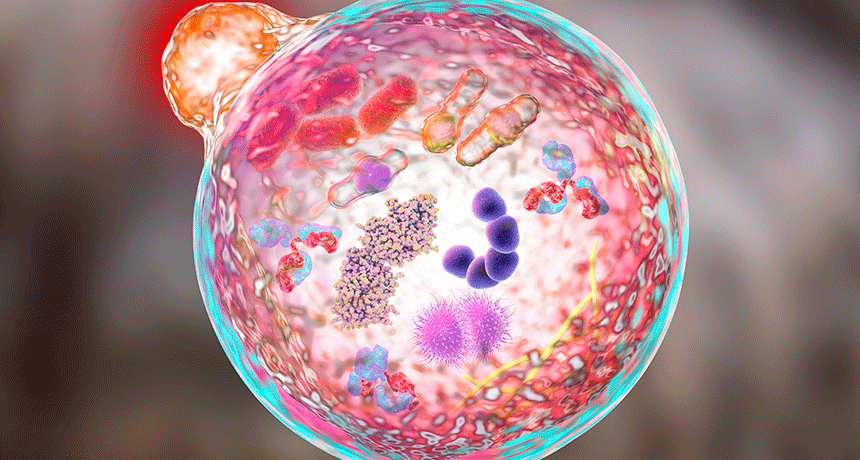 Life
LifeScientists Say: Metabolism
Metabolism is all the chemical activities that support life in a cell, an organ and a whole organism’s body.
-
 Fossils
FossilsA skeleton named ‘Little Foot’ causes big debate
New studies suggest a fossil hominid called Little Foot belongs to the species Australopithecus prometheus. Other scientists question whether such a species exists.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyRising seas threaten thousands of world cultural sites
Sea level rise threatens many thousands of cultural and archeological sites around the world.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGoose bumps may have hairy benefits
The nerves and muscles needed to set your hair on end and produce goose bumps also play a role in hair growth, new rodent data show. This suggests goose bumps might be useful in promoting hair growth.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAnalyze This: Most teen girls don’t meet guidelines for daily exercise
Girls trail boys in the amount of exercise they tend to get each day regardless of race.
-
 Brain
BrainMarijuana use may affect decision-making areas in teen brains
Marijuana use during adolescence may damage decision-making areas of the brain, according to a new study in rats.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHere’s the science you loved in 2018
When our readers read about science, they want to read about research that hits close to home, like smartphones, chocolate, vaping and more.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyICYMI: 2018’s top science offerings
From gene-edited babies to firenados and lavanados, this year offered both stunning news and curiosities in the world of science and research.
By Janet Raloff -
 Oceans
OceansWhat makes Aquaman special? He can take a lot of pressure
The new Aquaman movie makes life under the sea look pretty glamorous. In fact, we puny humans probably couldn’t take the pressure.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKeeping an irregular schedule may change how many calories you burn
Our daily cycle of calorie burning is one of many body processes that follow a biological clock.