Humans
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Lactose
You might not think of dairy products having sugar, but they do. Milk is rich in a sugar called lactose.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyBullying alters ‘bugs’ in the gut, hamster data show
A new study found that the microbes in a hamster’s gut changed in response to social stress.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFinding and helping teens for whom sadness is a disease
Adolescents should soon be screened for depression at their yearly check-up with their doctor.
-
 Climate
ClimateAnalyze This: Climate change could make food less healthy
Levels of important nutrients are lower in crops exposed to high levels of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas. How high? Try levels expected to be typical 30 years from now.
-
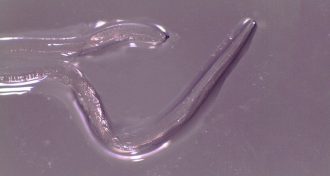 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWoman’s eye hosts more than a dozen cattle eyeworms
Oregon woman is the first human known to become infected with a cattle eyeworm known as Thelazia gulosa.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSleep helps wounds heal faster
Getting enough sleep may be more important for helping wounds heal than getting good nutrition, a new study finds.
By Ilima Loomis -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes don’t need nicotine to be toxic
E-cigarettes without nicotine can still be toxic. New studies find the flavorings in e-cigarettes can harm cells of the human immune system.
-
 Tech
TechRobots may soon actively crawl through your gut
Doctors are working with engineers to develop robotic tools that can crawl through the body to deliver medicine or scout for signs of disease.
By Eric Niiler -
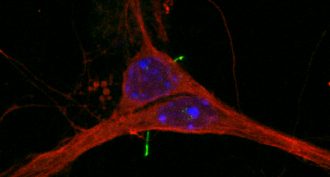 Brain
BrainTeeny tiny hairs on brain cells could have big jobs
Brain cells have tiny antennae called cilia. But no one really seemed to know what they did. Now, scientists have shown they could play a role in obesity.
-
 Brain
BrainScientists Say: Receptor
This molecule is a chemical messenger’s docking station. A receptor serves as a lock for cell activity.
-
 Brain
BrainCool Jobs: Decoding how your brain ‘reads’
For some stroke victims and people with dyslexia, reading is nearly impossible. These researchers are working to understand why.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow the body protects us from potentially toxic amounts of sugar
A study in mice shows the small intestine shields the liver from the potentially damaging effects of exposure to fructose — but only up to a limit.