Humans
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealing the world with science and medicine
Some people fear bacteria. Not these women. They are fighting disease with every tool science can give them.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentLaundering clothes may send indoor pollutants outdoors
Clothing absorbs pollutants from indoor air. During washing and drying, the fabric releases those chemicals into the outdoor environment, a new study finds.
-
 Earth
EarthNicotine from smoke enters body through the skin
Scientists have shown for the first time that nicotine from cigarette smoke can enter the body through bare skin from the air or contact with smoky clothes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGirls take note: Corn fiber can strengthen bones
Two new studies show that soluble corn fiber could help women improve bone health.
By Dinsa Sachan -
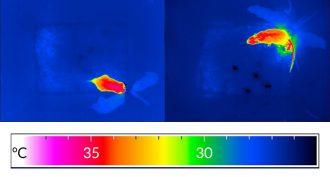 Brain
BrainMice brains hint at how bodies keep their cool
Nerve cells in mice can keep the body cool and may prevent high fevers. The discovery could have implications for obesity and other health issues.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyBe true to yourself, even in the face of opposition
It might seem easier to go with the flow when others disagree with you. But expressing your true opinion can be a positive experience, new data show.
-
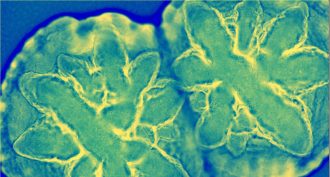 Microbes
MicrobesMouth germs team up to boost disease risk
The oxygen given off by harmless mouth bacteria can help disease-causing invaders grow strong and flourish.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. to outlaw antibacterial soaps
Soaps with germ-killing compounds promise cleaner hands. But manufacturers couldn’t show they offer any safety advantage. Now the U.S. government is banning them.
By Helen Thompson and Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis supplement makes calorie-rich foods less tempting
A supplement that contains the fatty acid propionate causes the brain to rate high-calorie foods less appealing.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCool Jobs: Linking animal health to human health
Scientists who watch out for diseases in wild animals also can play a role in keeping people from getting sick.
By Liz Devitt -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGrandparents’ diet could be a weighty issue for grandkids
Australian scientists have found that fat mice can pass on a heightened risk of obesity to their sons and grandsons.
By Dinsa Sachan -
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: What is epigenetics?
Epigenetics is the study of molecular “switches” that turn genes on and off. Tweak those switches and there could be big health consequences.
By Janet Raloff