Humans

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Humans
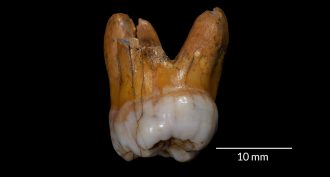
HumansNews Brief: Ancient teeth point to Neandertal relatives
New analyses of some teeth found in Siberia indicate that Neandertal cousins known as Denisovans lived there for at least 60,000 years. That would have had them around the same place as modern humans — and at nearly the same time.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistrySome 3-D printing can leave toxic taint
The ”ink” inside some 3-D printers can leave toxic traces. In tests, these chemicals harmed baby fish. But lighting could render the parts safer.
-
 Animals
AnimalsProfile: A human touch for animals
Temple Grandin uses her own autism to understand how animals think. The animal scientist is famous for fostering the humane treatment of livestock.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy equates sleepless nights with high-fat diet
Getting too little sleep has the same effect on blood sugar as eating high-fat foods, a study in dogs finds. This may set the body up for diabetes.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTable salt and shellfish can contain plastic
Bits of plastic have turned up in sea salts purchased in Chinese supermarkets. The finding suggests all sea salts may be similarly tainted. Shellfish too.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNews Brief: Group dancing helps teens bond
Coordinated dance routines help teens bond with one another, new data show. Group dancing also offers other benefits, including a higher threshold for pain.
By Janet Raloff -
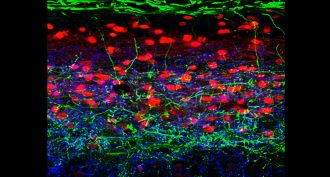 Life
LifeScientists discover itch-busting cells
A study in mice finds the body has a special way of dealing with an itch that’s caused by a light touch. The results could lead to treatments for chronic itch.
-
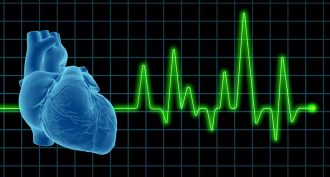 Tech
TechLight can control waves in heart tissue
Researchers have used light to trigger and control electrical waves in the heart. The technique might one day provide new ways to treat heart disease.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySome air pollutants seep through skin
The skin is the body’s largest organ. And it can let in as much or more of certain air pollutants than enter through the lungs, a new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
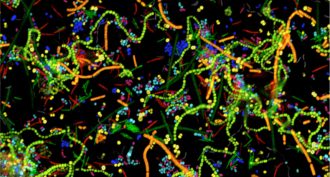 Microbes
MicrobesSlime cities
Biofilms are like tiny cities of bacteria — some harmless, others destructive. Scientists are learning how to keep these microscopic metropolises under control.
-
 Brain
BrainLessons from failure: Why we try, try again
We all suffer failures. But we don’t always try again. Focusing on what they can be learned might help people keep going, brain imaging data now show.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe earliest evidence of plague
Plague is best known as the killer disease that wiped out nearly half of Europe during the 1300s. But the germ infected people up to 3,000 years earlier than that, DNA from ancient teeth now show.
By Bruce Bower