Humans

Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTeen researcher eyes peripheral vision
Our peripheral vision helps us work and play. A student scientist studied how the distance between our eyes affects what we can see on the outer edges of our field of view.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDo mosquitoes love you? Blame your parents
By studying twins, scientists found that how attractive we are to mosquitoes depends partly on our genes. That could lead to better bug repellents.
-
 Brain
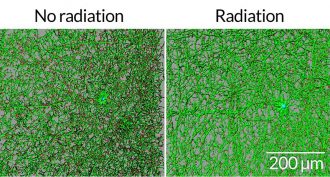
BrainTrip to Mars could damage astronauts’ brains
Experiments in mice suggest the high-energy particles that would zap astronauts on a mission to Mars could leave the explorers with brain damage.
-
 Health & Medicine
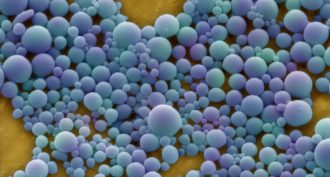
Health & MedicineInjected nanoparticles treat internal wounds
Soldiers wounded in a bombing could be treated with a shot of specially designed nanoparticles that stop bleeding and inflammation in the lungs.
-
 Fossils
FossilsRitual cannibalism occurred in Stone Age England
Stone Age human bones from a cave in England show signs of cannibalism. The people had been eaten during burial rituals nearly 15,000 years ago, experts say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
TechLaser vision reveals hidden worlds
From discovering ancient ruins to forecasting climate change, the laser mapping technology called lidar is changing many fields of science.
-
 Microbes
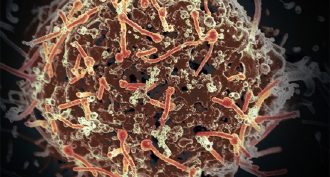
MicrobesNews Brief: Ebola’s dead stay infectious for a week
The Ebola virus doesn’t die with its victims — at least not right away. A corpse may host live virus for up to a week after death, a new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
 Health & Medicine
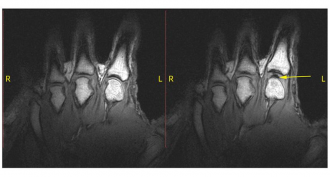
Health & MedicineMystery solved: Why knuckles crack
Scientists have puzzled over what makes that loud sound when our knuckles “crack.” Bubbles appear to play a role, but not in popping.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists Say: Hormone
This is a chemical that travels in the blood and acts as a signal. It can tell distant body parts what to do. When a chemical acts in this way, it has a special name.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMovies may tempt teens to drink
British 15-year-olds were more likely to binge-drink or have alcohol-related problems if they watched movies with plenty of onscreen drinking.
-
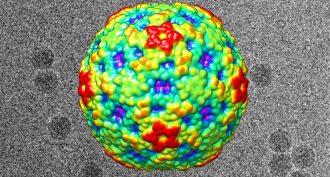 Microbes
MicrobesNew virus may have given kids polio-like symptoms
More than 100 U.S. children developed a paralyzing illness in 2014. Genetic evidence now suggests that the most likely culprit is a new form of a virus in the polio family.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking wastes may be toxic, tests show
Fracking operations have been polluting the environment. Some wastes have hormonal effects. Studies in mice now show that prenatal exposures to these wastes can trigger subtle but disturbing organ impacts.
By Beth Mole